Stoichiometry of the redox neutral deamination and oxidative dehydrogenation reactions catalyzed by the radical SAM enzyme DesII
- PMID: 20121093
- PMCID: PMC2833275
- DOI: 10.1021/ja909451a
Stoichiometry of the redox neutral deamination and oxidative dehydrogenation reactions catalyzed by the radical SAM enzyme DesII
Abstract
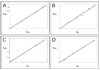
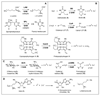
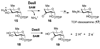
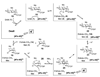
DesII from Streptomyces venezuelae is a radical SAM (S-adenosyl-l-methionine) enzyme that catalyzes the deamination of TDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-d-glucose to form TDP-3-keto-4,6-dideoxy-d-glucose in the biosynthesis of TDP-d-desosamine. DesII also catalyzes the dehydrogenation of the nonphysiological substrate TDP-D-quinovose to TDP-3-keto-6-deoxy-d-glucose. These properties prompted an investigation of how DesII handles SAM in the redox neutral deamination versus the oxidative dehydrogenation reactions. This work was facilitated by the development of an enzymatic synthesis of TDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-d-glucose that couples a transamination equilibrium to the thermodynamically favorable oxidation of formate. In this study, DesII is found to consume SAM versus TDP-sugar with stoichiometries of 0.96 +/- 0.05 and 1.01 +/- 0.05 in the deamination and dehydrogenation reactions, respectively, using Na(2)S(2)O(4) as the reductant. Importantly, no significant change in stoichiometry is observed when the flavodoxin/flavodoxin NADP(+) oxidoreductase/NADPH reducing system is used in place of Na(2)S(2)O(4). Moreover, there is no evidence of an uncoupled or abortive process in the deamination reaction, as indicated by the observation that dehydrogenation can take place in the absence of an external source of reductant whereas deamination cannot. Mechanistic and biochemical implications of these results are discussed.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Mechanistic studies of the radical S-adenosyl-L-methionine enzyme DesII: EPR characterization of a radical intermediate generated during its catalyzed dehydrogenation of TDP-D-quinovose.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 May 18;133(19):7292-5. doi: 10.1021/ja201212f. Epub 2011 Apr 22. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 21513273 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and mechanistic studies of DesII: a radical S-adenosyl-L-methionine enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of TDP-D-desosamine.J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Oct 7;131(39):14030-42. doi: 10.1021/ja903354k. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19746907 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Implications of the Deamination of TDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-d-fucose Catalyzed by the Radical SAM Enzyme DesII.Biochemistry. 2018 Jun 5;57(22):3130-3133. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00110. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29473739 Free PMC article.
-
Radical SAM enzymes in the biosynthesis of sugar-containing natural products.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Nov;1824(11):1231-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.11.006. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22172915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of Radical Initiation in the Radical S-Adenosyl-l-methionine Superfamily.Acc Chem Res. 2018 Nov 20;51(11):2611-2619. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00356. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Acc Chem Res. 2018. PMID: 30346729 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Not all 5'-deoxyadenosines are created equal: Tracing the provenance of 5'-deoxyadenosine formed by the radical S-adenosyl-L-methionine enzyme 7-carboxy-7-deazaguanine synthase.J Biol Chem. 2025 Apr;301(4):108347. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108347. Epub 2025 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40015645 Free PMC article.
-
Further characterization of Cys-type and Ser-type anaerobic sulfatase maturating enzymes suggests a commonality in the mechanism of catalysis.Biochemistry. 2013 Apr 30;52(17):2874-87. doi: 10.1021/bi400136u. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23477283 Free PMC article.
-
X-ray analysis of butirosin biosynthetic enzyme BtrN redefines structural motifs for AdoMet radical chemistry.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Oct 1;110(40):15949-54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312228110. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24048029 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Diversity of HemN-like Proteins.ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2022 Jan 18;2(2):109-119. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.1c00058. eCollection 2022 Apr 20. ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2022. PMID: 37101745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reaction Catalyzed by GenK, a Cobalamin-Dependent Radical S-Adenosyl-l-methionine Methyltransferase in the Biosynthetic Pathway of Gentamicin, Proceeds with Retention of Configuration.J Am Chem Soc. 2017 Nov 15;139(45):16084-16087. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b09890. Epub 2017 Nov 7. J Am Chem Soc. 2017. PMID: 29091410 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

