Natural products version 2.0: connecting genes to molecules
- PMID: 20121095
- PMCID: PMC2828520
- DOI: 10.1021/ja909118a
Natural products version 2.0: connecting genes to molecules
Abstract
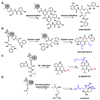
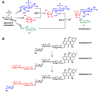
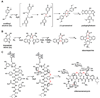
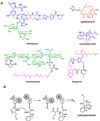
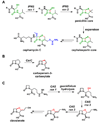
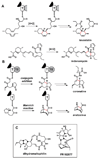
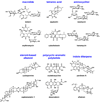
Natural products have played a prominent role in the history of organic chemistry, and they continue to be important as drugs, biological probes, and targets of study for synthetic and analytical chemists. In this Perspective, we explore how connecting Nature's small molecules to the genes that encode them has sparked a renaissance in natural product research, focusing primarily on the biosynthesis of polyketides and non-ribosomal peptides. We survey monomer biogenesis, coupling chemistries from templated and non-templated pathways, and the broad set of tailoring reactions and hybrid pathways that give rise to the diverse scaffolds and functionalization patterns of natural products. We conclude by considering two questions: What would it take to find all natural product scaffolds? What kind of scientists will be studying natural products in the future?
Figures




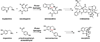


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

