The unfulfilled gene is required for the development of mushroom body neuropil in Drosophila
- PMID: 20122139
- PMCID: PMC2829026
- DOI: 10.1186/1749-8104-5-4
The unfulfilled gene is required for the development of mushroom body neuropil in Drosophila
Abstract
Background: The mushroom bodies (MBs) of Drosophila are required for complex behaviors and consist of three types of neurons, gamma, alpha'/beta' and alpha/beta. Previously, roles for transcription factors in MB neuronal differentiation have only been described for a subset of MB neurons. We are investigating the roles of unfulfilled (unf; HR51, CG16801) in MB development. unf encodes a nuclear receptor that is orthologous to the nuclear receptors fasciculation of axons defective 1 (FAX-1) of the nematode and photoreceptor specific nuclear receptor (PNR) of mammals. Based on our previous observations that unf transcripts accumulate in MB neurons at all developmental stages and the presence of axon pathfinding defects in fax-1 mutants, we hypothesized that unf regulates MB axon growth and pathfinding.
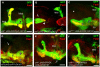
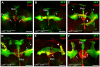
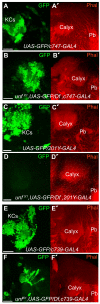
Results: We show that unf mutants exhibit a range of highly penetrant axon stalling phenotypes affecting all neurons of the larval and adult MBs. Phenotypic analysis of unfX1 mutants revealed that alpha'/beta' and alpha/beta neurons initially project axons but stall prior to the formation of medial or dorsal MB lobes. unfZ0001 mutants form medial lobes, although these axons fail to branch, which results in a failure to form the alpha or alpha' dorsal lobes. In either mutant background, gamma neurons fail to develop larval-specific dorsal projections. These mutant gamma neurons undergo normal pruning, but fail to re-extend axons medially during pupal development. unfRNAi animals displayed phenotypes similar to those seen in unfZ0001 mutants. Unique asymmetrical phenotypes were observed in unfX1/unfZ0001 compound heterozygotes. Expression of UAS-unf transgenes in MB neurons rescues the larval and adult unf mutant phenotypes.
Conclusions: These data support the hypothesis that unf plays a common role in the development of all types of MB neurons. Our data indicate that unf is necessary for MB axon extension and branching and that the formation of dorsal collaterals is more sensitive to the loss of unf function than medial projections. The asymmetrical phenotypes observed in compound heterozygotes support the hypothesis that the earliest MB axons may serve as pioneers for the later-born MB neurons, providing evidence for pioneer MB axon guidance in post-embryonic development.
Figures


References
-
- Lee T, Lee A, Luo L. Development of the Drosophila mushroom bodies: sequential generation of three distinct types of neurons from a neuroblast. Development. 1999;126:4065–4076. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

