Axin downregulates TCF-4 transcription via beta-catenin, but not p53, and inhibits the proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells
- PMID: 20122174
- PMCID: PMC2827467
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-25
Axin downregulates TCF-4 transcription via beta-catenin, but not p53, and inhibits the proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells
Abstract
Background: We previously reported that overexpression of Axin downregulates T cell factor-4 (TCF-4) transcription. However, the mechanism(s) by which Axin downregulates the transcription and expression of TCF-4 is not clear. It has been reported that beta-catenin promotes and p53 inhibits TCF-4 transcription, respectively. The aim of this study was to investigate whether beta-catenin and/or p53 is required for Axin-mediated downregulation of TCF-4.
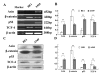
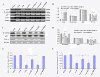
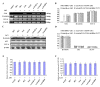
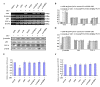
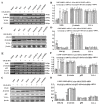
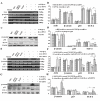
Results: Axin mutants that lack p53/HIPK2 and/or beta-catenin binding domains were expressed in lung cancer cells, BE1 (mutant p53) and A549 (wild type p53). Expression of Axin or AxinDeltap53 downregulates beta-catenin and TCF-4, and knock-down of beta-catenin upregulates TCF-4 in BE1 cells. However, expression of AxinDeltabeta-ca into BE1 cells did not downregulate TCF-4 expression. These results indicate that Axin downregulates TCF-4 transcription via beta-catenin. Although overexpression of wild-type p53 also downregulates TCF-4 in BE1 cells, cotransfection of p53 and AxinDeltabeta-ca did not downregulate TCF-4 further. These results suggest that Axin does not promote p53-mediated downregulation of TCF-4. Axin, AxinDeltap53, and AxinDeltabeta-ca all downregulated beta-catenin and TCF-4 in A549 cells. Knock-down of p53 upregulated beta-catenin and TCF-4, but cotransfection of AxinDeltabeta-ca and p53 siRNA resulted in downregulation of beta-catenin and TCF-4. These results indicate that p53 is not required for Axin-mediated downregulation of TCF-4. Knock-down or inhibition of GSK-3beta prevented Axin-mediated downregulation of TCF-4. Furthermore, expression of Axin and AxinDeltap53, prevented the proliferative and invasive ability of BE1 and A549, expression of AxinDeltabeta-ca could only prevented the proliferative and invasive ability effectively.
Conclusions: Axin downregulates TCF-4 transcription via beta-catenin and independently of p53. Axin may also inhibits the proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells via beta-catenin and p53.
Figures


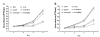

References
-
- Lustig B, Behrens J. The Wnt signaling pathway and its role in tumor development. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2003;129:199–221. - PubMed
-
- Ueta T, Ikeguchi M, Hirooka Y, Kaibara N, Terada T. Beta-catenin and cyclin D1 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2002;9:1197–1203. - PubMed
-
- Cheng XX, Sun Y, Chen XY, Zhang KL, Kong QY, Liu J, Li H. Frequent translocalization of beta-catenin in gastric cancers and its relevance to tumor progression. Oncol Rep. 2004;11:1201–1207. - PubMed
-
- Xu HT, Wang L, Lin D, Liu Y, Liu N, Yuan XM, Wang EH. Abnormal beta-catenin and reduced axin expression are associated with poor differentiation and progression in non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006;125:534–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

