Efficient protein alignment algorithm for protein search
- PMID: 20122207
- PMCID: PMC3009506
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-S1-S34
Efficient protein alignment algorithm for protein search
Abstract
Background: Proteins show a great variety of 3D conformations, which can be used to infer their evolutionary relationship and to classify them into more general groups; therefore protein structure alignment algorithms are very helpful for protein biologists. However, an accurate alignment algorithm itself may be insufficient for effective discovering of structural relationships among tens of thousands of proteins. Due to the exponentially increasing amount of protein structural data, a fast and accurate structure alignment tool is necessary to access protein classification and protein similarity search; however, the complexity of current alignment algorithms are usually too high to make a fully alignment-based classification and search practical.
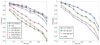
Results: We have developed an efficient protein pairwise alignment algorithm and applied it to our protein search tool, which aligns a query protein structure in the pairwise manner with all protein structures in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) to output similar protein structures. The algorithm can align hundreds of pairs of protein structures in one second. Given a protein structure, the tool efficiently discovers similar structures from tens of thousands of structures stored in the PDB always in 2 minutes in a single machine and 20 seconds in our cluster of 6 machines. The algorithm has been fully implemented and is accessible online at our webserver, which is supported by a cluster of computers.
Conclusion: Our algorithm can work out hundreds of pairs of protein alignments in one second. Therefore, it is very suitable for protein search. Our experimental results show that it is more accurate than other well known protein search systems in finding proteins which are structurally similar at SCOP family and superfamily levels, and its speed is also competitive with those systems. In terms of the pairwise alignment performance, it is as good as some well known alignment algorithms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Search similar protein structures with classification, sequence and 3d alignments.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2009 Oct;7(5):755-71. doi: 10.1142/s021972000900431x. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2009. PMID: 19785044
-
Large-scale comparison of protein sequence alignment algorithms with structure alignments.Proteins. 2000 Jul 1;40(1):6-22. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0134(20000701)40:1<6::aid-prot30>3.0.co;2-7. Proteins. 2000. PMID: 10813826
-
Automatic classification of protein structures using low-dimensional structure space mappings.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014;15 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-S2-S1. Epub 2014 Jan 24. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24564500 Free PMC article.
-
mTM-align: an algorithm for fast and accurate multiple protein structure alignment.Bioinformatics. 2018 May 15;34(10):1719-1725. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx828. Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29281009 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of proteins based on segments structural similarity.Acta Biochim Pol. 2004;51(1):161-72. Acta Biochim Pol. 2004. PMID: 15094837 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic programming used to align protein structures with a spectrum is robust.Biology (Basel). 2013 Nov 20;2(4):1296-310. doi: 10.3390/biology2041296. Biology (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24833226 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fischer D, Nussinov R, Wolfson H. 3D substructure matching in protein molecules. Proc 3rd Intl Symp Combinatorial Pattern Matching, Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 1992;644:136–150.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

