Comparative classification of species and the study of pathway evolution based on the alignment of metabolic pathways
- PMID: 20122211
- PMCID: PMC3009510
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-S1-S38
Comparative classification of species and the study of pathway evolution based on the alignment of metabolic pathways
Abstract
Background: Pathways provide topical descriptions of cellular circuitry. Comparing analogous pathways reveals intricate insights into individual functional differences among species. While previous works in the field performed genomic comparisons and evolutionary studies that were based on specific genes or proteins, whole genomic sequence, or even single pathways, none of them described a genomic system level comparative analysis of metabolic pathways. In order to properly implement such an analysis one should overcome two specific challenges: how to combine the effect of many pathways under a unified framework and how to appropriately analyze co-evolution of pathways. Here we present a computational approach for solving these two challenges. First, we describe a comprehensive, scalable, information theory based computational pipeline that calculates pathway alignment information and then compiles it in a novel manner that allows further analysis. This approach can be used for building phylogenies and for pointing out specific differences that can then be analyzed in depth. Second, we describe a new approach for comparing the evolution of metabolic pathways. This approach can be used for detecting co-evolutionary relationships between metabolic pathways.
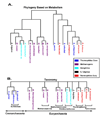
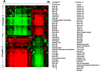
Results: We demonstrate the advantages of our approach by applying our pipeline to data from the MetaCyc repository (which includes a total of 205 organisms and 660 metabolic pathways). Our analysis revealed several surprising biological observations. For example, we show that the different habitats in which Archaea organisms reside are reflected by a pathway based phylogeny. In addition, we discover two striking clusters of metabolic pathways, each cluster includes pathways that have very similar evolution.
Conclusion: We demonstrate that distance measures that are based on the topology and the content of metabolic networks are useful for studying evolution and co-evolution.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phylogeny of metabolic networks: a spectral graph theoretical approach.J Biosci. 2015 Oct;40(4):799-808. doi: 10.1007/s12038-015-9562-0. J Biosci. 2015. PMID: 26564980
-
Phylogenetic analysis based on genome-scale metabolic pathway reaction content.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004 Aug;65(2):203-10. doi: 10.1007/s00253-004-1641-3. Epub 2004 Jun 9. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 15197509
-
Ancestral state reconstruction of metabolic pathways across pangenome ensembles.Microb Genom. 2020 Nov;6(11):mgen000429. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000429. Microb Genom. 2020. PMID: 32924924 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial genome analysis: the COG approach.Brief Bioinform. 2019 Jul 19;20(4):1063-1070. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx117. Brief Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 28968633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The unique features of glycolytic pathways in Archaea.Biochem J. 2003 Oct 15;375(Pt 2):231-46. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021472. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12921536 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reconstruction of phyletic trees by global alignment of multiple metabolic networks.BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-S2-S12. Epub 2013 Jan 21. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23368411 Free PMC article.
-
Computational model for pathway reconstruction to unravel the evolutionary significance of melanin synthesis.Bioinformation. 2013;9(2):94-100. doi: 10.6026/97320630009094. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Bioinformation. 2013. PMID: 23390353 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstructing phylogeny from metabolic substrate-product relationships.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011 Feb 15;12 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S27. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-S1-S27. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21342557 Free PMC article.
-
Control Theory and Systems Biology: Potential Applications in Neurodegeneration and Search for Therapeutic Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 27;25(1):365. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010365. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconstructing Phylogeny by Aligning Multiple Metabolic Pathways Using Functional Module Mapping.Molecules. 2018 Feb 23;23(2):486. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020486. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29473850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BioCarta. http://www.biocarta.com
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

