A novel approach for haplotype-based association analysis using family data
- PMID: 20122219
- PMCID: PMC3009518
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-S1-S45
A novel approach for haplotype-based association analysis using family data
Abstract
Background: Haplotype-based approaches have been extensively studied for case-control association mapping in recent years. It has been shown that haplotype methods can provide more consistent results comparing to single-locus based approaches, especially in cases where causal variants are not typed. Improved power has been observed by clustering similar or rare haplotypes into groups to reduce the degrees of freedom of association tests. For family-based association studies, one commonly used strategy is Transmission Disequilibrium Tests (TDT), which examine the imbalanced transmission of alleles/haplotypes to affected and normal children. Many extensions have been developed to deal with general pedigrees and continuous traits.
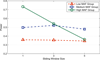
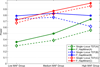
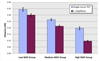
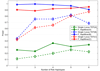
Results: In this paper, we propose a new haplotype-based association method for family data that is different from the TDT framework. Our approach (termed F_HapMiner) is based on our previous successful experiences on haplotype inference from pedigree data and haplotype-based association mapping. It first infers diplotype pairs of each individual in each pedigree assuming no recombination within a family. A phenotype score is then defined for each founder haplotype. Finally, F_HapMiner applies a clustering algorithm on those founder haplotypes based on their similarities and identifies haplotype clusters that show significant associations with diseases/traits. We have performed extensive simulations based on realistic assumptions to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed approach by considering different factors such as allele frequency, linkage disequilibrium (LD) structure, disease model and sample size. Comparisons with single-locus and haplotype-based TDT methods demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms the TDT-based approaches regardless of disease models, local LD structures or allele/haplotype frequencies.
Conclusion: We present a novel haplotype-based association approach using family data. Experiment results demonstrate that it achieves significantly higher power than TDT-based approaches.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The power comparison of the haplotype-based collapsing tests and the variant-based collapsing tests for detecting rare variants in pedigrees.BMC Genomics. 2014 Jul 28;15(1):632. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-632. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25070353 Free PMC article.
-
Haplotype-based quantitative trait mapping using a clustering algorithm.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 May 18;7:258. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-258. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16709248 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission/disequilibrium test meets measured haplotype analysis: family-based association analysis guided by evolution of haplotypes.Am J Hum Genet. 2001 May;68(5):1250-63. doi: 10.1086/320110. Epub 2001 Apr 10. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11309689 Free PMC article.
-
The trimmed-haplotype test for linkage disequilibrium.Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Mar;66(3):1062-75. doi: 10.1086/302796. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. PMID: 10712218 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission/disequilibrium test based on haplotype sharing for tightly linked markers.Am J Hum Genet. 2003 Sep;73(3):566-79. doi: 10.1086/378205. Epub 2003 Aug 15. Am J Hum Genet. 2003. PMID: 12929082 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The follicular outcome after standard gonadotropin stimulation is associated with ERα and ERβ genotypes.Endocrine. 2014 Dec;47(3):930-5. doi: 10.1007/s12020-014-0249-3. Epub 2014 Apr 5. Endocrine. 2014. PMID: 24705910
-
Single Marker and Haplotype-Based Association Analysis of Semolina and Pasta Colour in Elite Durum Wheat Breeding Lines Using a High-Density Consensus Map.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 30;12(1):e0170941. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170941. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28135299 Free PMC article.
-
Using haplotypes for the prediction of allelic identity to fine-map QTL: characterization and properties.Genet Sel Evol. 2014 Jul 14;46(1):45. doi: 10.1186/1297-9686-46-45. Genet Sel Evol. 2014. PMID: 25022866 Free PMC article.
-
Use of diplotypes - matched haplotype pairs from homologous chromosomes - in gene-disease association studies.Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2014 Jun;26(3):165-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0829.2014.03.009. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25114493 Free PMC article.
-
Combining an evolution-guided clustering algorithm and haplotype-based LRT in family association studies.BMC Genet. 2011 May 19;12:48. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-12-48. BMC Genet. 2011. PMID: 21592403 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

