Formal reasoning on qualitative models of coinfection of HIV and Tuberculosis and HAART therapy
- PMID: 20122243
- PMCID: PMC3009541
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-S1-S67
Formal reasoning on qualitative models of coinfection of HIV and Tuberculosis and HAART therapy
Abstract
Background: Several diseases, many of which nowadays pandemic, consist of multifactorial pathologies. Paradigmatic examples come from the immune response to pathogens, in which cases the effects of different infections combine together, yielding complex mutual feedback, often a positive one that boosts infection progression in a scenario that can easily become lethal. HIV is one such infection, which weakens the immune system favouring the insurgence of opportunistic infections, amongst which Tuberculosis (TB). The treatment with antiretroviral therapies has shown effective in reducing mortality. An in-depth understanding of complex systems, like the one consisting of HIV, TB and related therapies, is an open great challenge, on the boundaries of bioinformatics, computational and systems biology.
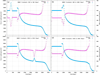
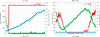
Results: We present a simplified formalisation of the highly dynamic system consisting of HIV, TB and related therapies, at the cellular level. The progression of the disease (AIDS) depends hence on interactions between viruses, cells, chemokines, the high mutation rate of viruses, the immune response of individuals and the interaction between drugs and infection dynamics. We first discuss a deterministic model of dual infection (HIV and TB) which is able to capture the long-term dynamics of CD4 T cells, viruses and Tumour Necrosis Factor (TNF). We contrast this model with a stochastic approach which captures intrinsic fluctuations of the biological processes. Furthermore, we also integrate automated reasoning techniques, i.e. probabilistic model checking, in our formal analysis. Beyond numerical simulations, model checking allows general properties (effectiveness of anti-HIV therapies) to be verified against the models by means of an automated procedure. Our work stresses the growing importance and flexibility of model checking techniques in bioinformatics. In this paper we i) describe HIV as a complex case of infectious diseases; ii) provide a number of different formal descriptions that suitably account for aspects of interests; iii) suggest that the integration of different models together with automated reasoning techniques can improve the understanding of infections and therapies through formal analysis methodologies.
Conclusion: We argue that the described methodology suitably supports the study of viral infections in a formal, automated and expressive manner. We envisage a long-term contribution of this kind of approaches to clinical Bioinformatics and Translational Medicine.
Figures
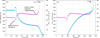

Similar articles
-
Immunological recovery in tuberculosis/HIV co-infected patients on antiretroviral therapy: implication for tuberculosis preventive therapy.BMC Infect Dis. 2017 Jul 25;17(1):517. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2627-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28743248 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of cellular immunity against tuberculosis in patients coinfected with HIV-1 and tuberculosis with effective antiretroviral therapy: assessment by determination of CD69 expression on T cells after tuberculin stimulation.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2000 Nov 1;25(3):212-20. doi: 10.1097/00126334-200011010-00002. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2000. PMID: 11115951
-
A Markov model for the effects of virological failure on HIV/AIDS progression in tuberculosis co-infected patients receiving antiretroviral therapy in a rural clinic in northern South Africa.S Afr Med J. 2020 Mar 30;110(4):313-319. doi: 10.7196/SAMJ.2020.v110i4.13934. S Afr Med J. 2020. PMID: 32657744
-
Molecular and cellular interactions of HIV-1/HTLV coinfection and impact on AIDS progression.AIDS Rev. 2007 Jul-Sep;9(3):140-9. AIDS Rev. 2007. PMID: 17982939 Review.
-
Improving survival with tuberculosis & HIV treatment integration: A mini-review.Indian J Med Res. 2019 Aug;150(2):131-138. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_660_19. Indian J Med Res. 2019. PMID: 31670268 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Changing risk behaviours and the HIV epidemic: a mathematical analysis in the context of treatment as prevention.PLoS One. 2013 May 6;8(5):e62321. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062321. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23671592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gillespie DT. Exact Stochastic Simulation of Coupled Chemical Reactions. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 1977;81(25):2340–2361. doi: 10.1021/j100540a008. - DOI
-
- Nowak MA, May RM. Virus dynamics. mathematical principles of immunology and virology. Oxford University Press; 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

