Optimized high gradient magnetic separation for isolation of Plasmodium-infected red blood cells
- PMID: 20122252
- PMCID: PMC2831011
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-9-38
Optimized high gradient magnetic separation for isolation of Plasmodium-infected red blood cells
Abstract
Background: Highly purified infected red blood cells (irbc), or highly synchronized parasite cultures, are regularly required in malaria research. Conventional isolation and synchronization rely on density and osmotic fragility of irbc, respectively. High gradient magnetic separation (HGMS) offers an alternative based on intrinsic magnetic properties of irbc, avoiding exposure to chemicals and osmotic stress. Successful HGMS concentration in malaria research was previously reported using polymer coated columns, while HGMS depletion has not been described yet. This study presents a new approach to both HGMS concentration and depletion in malaria research, rendering polymer coating unnecessary.
Methods: A dipole magnet generating a strong homogenous field was custom assembled. Polypropylene syringes were fitted with one-way stopcocks and filled with stainless steel wool. Rbc from Plasmodium falciparum cultures were resuspended in density and viscosity optimized HGMS buffers and HGMS processed. Purification and depletion results were analysed by flow cytometer and light microscopy. Viability was evaluated by calculating the infection rate after re-culturing of isolates.
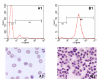
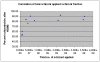
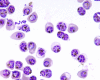
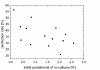
Results: In HGMS concentration, purity of irbc isolates from asynchronous cultures consistently ranged from 94.8% to 98.4% (mean 95.7%). With further optimization, over 90% of isolated irbc contained segmented schizonts. Processing time was less than 45 min. Reinfection rates ranged from 21.0% to 56.4%. In HGMS depletion, results were comparable to treatment with sorbitol, as demonstrated by essentially identical development of cultures.
Conclusion: The novel HGMS concentration procedure achieves high purities of segmented stage irbc from standard asynchronous cultures, and is the first HGMS depletion alternative to sorbitol lysis. It represents a simple and highly efficient alternative to conventional irbc concentration and synchronization methods.
Figures
References
-
- Kutner S, Breuer WV, Ginsburg H, Aley SB, Cabantchik ZI. Characterization of permeation pathways in the plasma membrane of human erythrocytes infected with early stages of Plasmodium falciparum: Association with parasite development. J Cell Physiol. 1985;125:521–527. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041250323. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Goodyer ID, Johnson J, Eisenthal R, Hayes DJ. Purification of mature-stage Plasmodium falciparum by gelatine flotation. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1994;88:209–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

