Reduced blood brain barrier breakdown in P-selectin deficient mice following transient ischemic stroke: a future therapeutic target for treatment of stroke
- PMID: 20122276
- PMCID: PMC2829030
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-11-12
Reduced blood brain barrier breakdown in P-selectin deficient mice following transient ischemic stroke: a future therapeutic target for treatment of stroke
Abstract
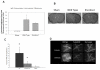
Background: The link between early blood- brain barrier (BBB) breakdown and endothelial cell activation in acute stroke remain poorly defined. We hypothesized that P-selectin, a mediator of the early phase of leukocyte recruitment in acute ischemia is also a major contributor to early BBB dysfunction following stroke. This was investigated by examining the relationship between BBB alterations following transient ischemic stroke and expression of cellular adhesion molecule P-selectin using a combination of magnetic resonance molecular imaging (MRMI), intravital microscopy and immunohistochemistry. MRMI was performed using the contrast, gadolinium diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (Gd-DTPA) conjugated to Sialyl Lewis X (Slex) where the latter is known to bind to activated endothelium via E- or P selectins. Middle cerebral artery occlusion was induced in male C57/BL 6 wild-type (WT) mice and P-selectin-knockout (KO) mice. At 24 hours following middle cerebral artery occlusion, T1 maps were acquired prior to and following contrast injection. In addition to measuring P- and E-selectin expression in brain homogenates, alterations in BBB function were determined immunohistochemically by assessing the extravasation of immunoglobulin G (IgG) or staining for polymorphonuclear (PMN) leukocytes. In vivo assessment of BBB dysfunction was also investigated optically using intravital microscopy of the pial circulation following the injection of Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC)-dextran (MW 2000 kDa).
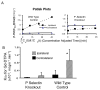
Results: MRI confirmed similar infarct sizes and T1 values at 24 hours following stroke for both WT and KO animals. However, the blood to brain transfer constant for Gd DTPA (Kgd) demonstrated greater tissue extravasation of Gd DTPA in WT animals than KO mice (P < 0.03). In the P selectin KO mice, Delta T1 stroke -Delta T1 contralateral control cortex, decreased significantly in the Gd-DTPA(sLeX) group compared to Gd-DTPA, indicative of sLeX mediated accumulation of the targeted contrast agent. Regarding BBB function, in the P-selectin KO mice compared to WT control mice, there was an attenuation in the extravasation of IgG (P < 0.001), a trend for decreased FITC extravasation and less infiltration of PMN leukocytes (P < 0.001) thereby supporting the observed increase in Kgd permeability in stroke brain of WT compared to KO mice.
Conclusion: P-selectin expression contributes to enhanced BBB dysfunction at 24 hours after transient focal cerebral ischemia.
Figures
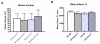

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

