Alteration of primary afferent activity following inferior alveolar nerve transection in rats
- PMID: 20122287
- PMCID: PMC2829527
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-9
Alteration of primary afferent activity following inferior alveolar nerve transection in rats
Abstract
Background: In order to evaluate the neural mechanisms underlying the abnormal facial pain that may develop following regeneration of the injured inferior alveolar nerve (IAN), the properties of the IAN innervated in the mental region were analyzed.
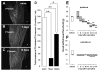
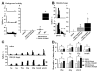
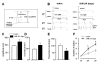
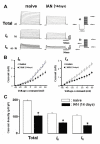
Results: Fluorogold (FG) injection into the mental region 14 days after IAN transection showed massive labeling of trigeminal ganglion (TG). The escape threshold to mechanical stimulation of the mental skin was significantly lower (i.e. mechanical allodynia) at 11-14 days after IAN transection than before surgery. The background activity, mechanically evoked responses and afterdischarges of IAN Adelta-fibers were significantly higher in IAN-transected rats than naive. The small/medium diameter TG neurons showed an increase in both tetrodotoxin (TTX)-resistant (TTX-R) and -sensitive (TTX-S) sodium currents (INa) and decrease in total potassium current, transient current (IA) and sustained current (IK) in IAN-transected rats. The amplitude, overshoot amplitude and number of action potentials evoked by the depolarizing pulses after 1 muM TTX administration in TG neurons were significantly higher, whereas the threshold current to elicit spikes was smaller in IAN-transected rats than naive. Resting membrane potential was significantly smaller in IAN-transected rats than that of naive.
Conclusions: These data suggest that the increase in both TTX-S INa and TTX-R INa and the decrease in IA and Ik in small/medium TG neurons in IAN-transected rats are involved in the activation of spike generation, resulting in hyperexcitability of Adelta-IAN fibers innervating the mental region after IAN transection.
Figures
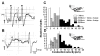

Similar articles
-
Modulation of trigeminal spinal subnucleus caudalis neuronal activity following regeneration of transected inferior alveolar nerve in rats.J Neurophysiol. 2008 May;99(5):2251-63. doi: 10.1152/jn.00794.2007. Epub 2008 Mar 12. J Neurophysiol. 2008. PMID: 18337368
-
Alteration of the second branch of the trigeminal nerve activity following inferior alveolar nerve transection in rats.Pain. 2004 Oct;111(3):323-334. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2004.07.014. Pain. 2004. PMID: 15363876
-
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound accelerates nerve regeneration following inferior alveolar nerve transection in rats.Eur J Oral Sci. 2016 Jun;124(3):246-50. doi: 10.1111/eos.12271. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Eur J Oral Sci. 2016. PMID: 27058986
-
The relationship between changes in the expression of growth associated protein-43 and functional recovery of the injured inferior alveolar nerve following transection without repair in adult rats.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015 Nov;43(9):1906-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2015.08.018. Epub 2015 Aug 28. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015. PMID: 26421471
-
Voltage-dependent conductances of solitary ganglion cells dissociated from the rat retina.J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:361-91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016497. J Physiol. 1987. PMID: 2443669 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trigeminal nerve injury ErbB3/ErbB2 promotes mechanical hypersensitivity.Anesthesiology. 2012 Aug;117(2):381-8. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3182604b2b. Anesthesiology. 2012. PMID: 22705569 Free PMC article.
-
Pain Management with Natural Products: Neurophysiological Insights.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 30;26(13):6305. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136305. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemokine CCL2 and its receptor CCR2 in the medullary dorsal horn are involved in trigeminal neuropathic pain.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Jul 9;9:136. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-136. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22721162 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of ERK phosphorylation of trigeminal spinal subnucleus caudalis neurons in thermal hypersensitivity in rats with infraorbital nerve injury.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57278. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057278. Epub 2013 Feb 22. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23451198 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical quercetin alleviates hyperexcitability of trigeminal nociceptive neurons associated with inflammatory hyperalgesia comparable to NSAIDs.Mol Pain. 2022 Apr;18:17448069221108971. doi: 10.1177/17448069221108971. Mol Pain. 2022. PMID: 35734996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luo L, Chang L, Brown SM, Ao H, Lee DH, Higuera ES, Dubin AE, Chaplan SR. Role of peripheral hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-modulated channel pacemaker channels in acute and chronic pain models in the rat. Neuroscience. 2007;144:1477–1485. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.10.048. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

