The Wilms' tumor suppressor protein WT1 is processed by the serine protease HtrA2/Omi
- PMID: 20122399
- PMCID: PMC2815029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.12.023
The Wilms' tumor suppressor protein WT1 is processed by the serine protease HtrA2/Omi
Abstract
The Wilms' tumor suppressor protein WT1 functions as a transcriptional regulator of genes controlling growth, apoptosis, and differentiation. It has become clear that WT1 can act as an oncogene in many tumors, primarily through the inhibition of apoptosis. Here, we identify the serine protease HtrA2 as a WT1 binding partner and find that it cleaves WT1 at multiple sites following the treatment of cells with cytotoxic drugs. Ablation of HtrA2 activity either by chemical inhibitor or by siRNA prevents the proteolysis of WT1 under apoptotic conditions. Moreover, the apoptosis-dependent cleavage of WT1 is defective in HtrA2 knockout cells. Proteolysis of WT1 by HtrA2 causes the removal of WT1 from its binding sites at gene promoters, leading to alterations in gene regulation that enhance apoptosis. Our findings provide insights into the function of HtrA2 in the regulation of apoptosis and the oncogenic activities of WT1.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
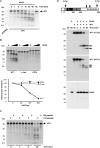
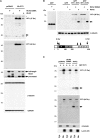
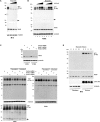
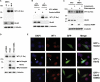
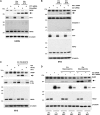
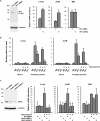
Comment in
-
WT1 the oncogene: a tale of death and HtrA.Mol Cell. 2010 Jan 29;37(2):153-5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.01.010. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20122396
-
WT1 as a substrate of HtrA2: a potential pathway for therapeutic targeting by HtrA proteases.Future Oncol. 2010 Aug;6(8):1233-5. doi: 10.2217/fon.10.84. Future Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20799869 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ariyaratana S., Loeb D.M. The role of the Wilms tumour gene (WT1) in normal and malignant haematopoiesis. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2007;9:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Cilenti L., Lee Y., Hess S., Srinivasula S., Park K.M., Junqueira D., Davis H., Bonventre J.V., Alnemri E.S., Zervos A.S. Characterization of a novel and specific inhibitor for the pro-apoptotic protease Omi/HtrA2. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:11489–11494. - PubMed
-
- Discenza M.T., Pelletier J. Insights into the physiological role of WT1 from studies of genetically modified mice. Physiol. Genomics. 2004;16:287–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

