Specific targeting to B cells by lipid-based nanoparticles conjugated with a novel CD22-ScFv
- PMID: 20122924
- PMCID: PMC2849008
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2010.01.006
Specific targeting to B cells by lipid-based nanoparticles conjugated with a novel CD22-ScFv
Abstract
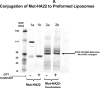
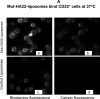
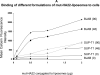
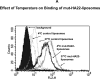
The CD22 antigen is a viable target for therapeutic intervention for B-cell lymphomas. Several therapeutic anti-CD22 antibodies as well as an anti-CD22-based immunotoxin (HA22) are currently under investigation in clinical settings. Coupling of anti-CD22 reagents with a nano-drug delivery vehicle is projected to significantly improve treatment efficacies. Therefore, we generated a mutant of the targeting segment of HA22 (a CD22 scFv) to increase its soluble expression (mut-HA22), and conjugated it to the surface of sonicated liposomes to generate immunoliposomes (mut-HA22-liposomes). We examined liposome binding and uptake by CD22(+) B-lymphocytes (BJAB) by using calcein and/or rhodamine PE-labeled liposomes. We also tested the effect of targeting on cellular toxicity with doxorubicin-loaded liposomes. We report that: (i) Binding of mut-HA22-liposomes to BJAB cells was significantly greater than liposomes not conjugated with mut-HA22 (control liposomes), and mut-HA22-liposomes bind to and are taken in by BJAB cells in a dose and temperature-dependent manner, respectively; (ii) This binding occurred via the interaction with the cellular CD22 as pre-incubation of the cells with mut-HA22 blocked subsequent liposome binding; (iii) Intracellular localization of mut-HA22-liposomes at 37 degrees C but not at 4 degrees C indicated that our targeted liposomes were taken up through an energy dependent process via receptor-mediated endocytosis; and (iv) Mut-HA22-liposomes loaded with doxorubicin exhibited at least 2-3 fold more accumulation of doxorubicin in BJAB cells as compared to control liposomes. Moreover, these liposomes showed at least a 2-4 fold enhanced killing of BJAB or Raji cells (CD22(+)), but not SUP-T1 cells (CD22(-)). Taken together these data suggest that these 2nd-generation liposomes may serve as promising carriers for targeted drug delivery to treat patients suffering from B-cell lymphoma.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures










Similar articles
-
The improvement of an anti-CD22 immunotoxin: conversion to single-chain and disulfide stabilized form and affinity maturation by alanine scan.MAbs. 2011 Sep-Oct;3(5):479-86. doi: 10.4161/mabs.3.5.17228. Epub 2011 Sep 1. MAbs. 2011. PMID: 22048691 Free PMC article.
-
A recombinant immunotoxin targeting CD22 with low immunogenicity, low nonspecific toxicity, and high antitumor activity in mice.J Immunother. 2010 Apr;33(3):297-304. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181cd1164. J Immunother. 2010. PMID: 20445350 Free PMC article.
-
Novel synthesizing method of pH-dependent doxorubicin-loaded anti-CD22-labelled drug delivery nanosystem.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Sep 7;9:5123-33. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S86764. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26379425 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting B lymphoma with nanoparticles bearing glycan ligands of CD22.Leuk Lymphoma. 2012 Feb;53(2):208-10. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2011.604755. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Leuk Lymphoma. 2012. PMID: 21756025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting CD22 in B-cell malignancies: current status and clinical outlook.BioDrugs. 2013 Aug;27(4):293-304. doi: 10.1007/s40259-013-0016-7. BioDrugs. 2013. PMID: 23696252 Review.
Cited by
-
Effective elimination of liver cancer stem-like cells by CD90 antibody targeted thermosensitive magnetoliposomes.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 14;7(24):35894-35916. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9116. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27145285 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted polymeric therapeutic nanoparticles: design, development and clinical translation.Chem Soc Rev. 2012 Apr 7;41(7):2971-3010. doi: 10.1039/c2cs15344k. Epub 2012 Mar 5. Chem Soc Rev. 2012. PMID: 22388185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A high-throughput lysosome trafficking assay guides ligand selection and elucidates differences in CD22-targeted nanodelivery.Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2024 May 13;25(1):2351791. doi: 10.1080/14686996.2024.2351791. eCollection 2024. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2024. PMID: 38817250 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidoid nanoparticle mediated silencing of Mcl-1 induces apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016 May;241(9):1007-13. doi: 10.1177/1535370216640944. Epub 2016 Mar 27. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016. PMID: 27022142 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-targeted nanocarriers for therapeutic delivery to cancer.Mol Membr Biol. 2010 Oct;27(7):286-98. doi: 10.3109/09687688.2010.521200. Mol Membr Biol. 2010. PMID: 21028937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tedder TF, Tuscano J, Sato S, Kehrl JH. CD22, a B lymphocyte-specific adhesion molecule that regulates antigen receptor signaling. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:481–504. - PubMed
-
- Shan D, Press OW. Constitutive endocytosis and degradation of CD22 by human B cells. J Immunol. 1995;154:4466–75. - PubMed
-
- Sato S, Tuscano JM, Inaoki M, Tedder TF. CD22 negatively and positively regulates signal transduction through the B lymphocyte antigen receptor. Semin Immunol. 1998;10:287–97. - PubMed
-
- Dorken B, Moldenhauer G, Pezzutto A, et al. HD39 (B3), a B lineage-restricted antigen whose cell surface expression is limited to resting and activated human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986;136:4470–9. - PubMed
-
- Schwarting R, Stein H, Wang CY. The monoclonal antibodies alpha S-HCL 1 (alpha Leu-14) and alpha S-HCL 3 (alpha Leu-M5) allow the diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 1985;65:974–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

