The structure and stability of the monomorphic HLA-G are influenced by the nature of the bound peptide
- PMID: 20122941
- PMCID: PMC2905647
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.01.052
The structure and stability of the monomorphic HLA-G are influenced by the nature of the bound peptide
Abstract
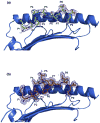
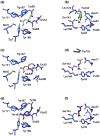
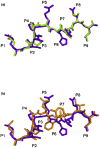
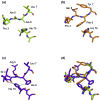
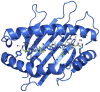
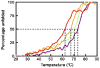
The highly polymorphic major histocompatibility complex class Ia (MHC-Ia) molecules present a broad array of peptides to the clonotypically diverse alphabeta T-cell receptors. In contrast, MHC-Ib molecules exhibit limited polymorphism and bind a more restricted peptide repertoire, in keeping with their major role in innate immunity. Nevertheless, some MHC-Ib molecules do play a role in adaptive immunity. While human leukocyte antigen E (HLA-E), the MHC-Ib molecule, binds a very restricted repertoire of peptides, the peptide binding preferences of HLA-G, the class Ib molecule, are less stringent, although the basis by which HLA-G can bind various peptides is unclear. To investigate how HLA-G can accommodate different peptides, we compared the structure of HLA-G bound to three naturally abundant self-peptides (RIIPRHLQL, KGPPAALTL and KLPQAFYIL) and their thermal stabilities. The conformation of HLA-G(KGPPAALTL) was very similar to that of the HLA-G(RIIPRHLQL) structure. However, the structure of HLA-G(KLPQAFYIL) not only differed in the conformation of the bound peptide but also caused a small shift in the alpha2 helix of HLA-G. Furthermore, the relative stability of HLA-G was observed to be dependent on the nature of the bound peptide. These peptide-dependent effects on the substructure of the monomorphic HLA-G are likely to impact on its recognition by receptors of both innate and adaptive immune systems.
Figures

References
-
- Tynan FE, Borg NA, Miles JJ, Beddoe T, El-Hassen D, Silins SL, et al. High resolution structures of highly bulged viral epitopes bound to major histocompatibility complex class I: implications for T-cell receptor engagement and T-cell immunodominance. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:23900–23909. - PubMed
-
- Grimsley C, Kawasaki A, Gassner C, Sageshima N, Nose Y, Hatake K, et al. Definitive high resolution typing of HLA-E allelic polymorphisms: identifying potential errors in existing allele data. Tissue Antigens. 2002;60:206–212. - PubMed
-
- Lajoie J, Boivin AA, Jeanneau A, Faucher MC, Roger M. Identification of six new HLA-G alleles with non-coding DNA base changes. Tissue Antigens. 2009;73:379–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

