Neurotensin receptor type 1 regulates ethanol intoxication and consumption in mice
- PMID: 20122953
- PMCID: PMC2830308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2010.01.012
Neurotensin receptor type 1 regulates ethanol intoxication and consumption in mice
Abstract
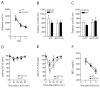
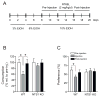
Neurotensin receptor type 1 (NTS1) is known to mediate a variety of biological functions of neurotensin (NT) in the central nervous system. In this study, we found that NTS1 null mice displayed decreased sensitivity to the ataxic effect of ethanol on the rotarod and increased ethanol consumption when given a free choice between ethanol and tap water containing bottles. Interestingly, the administration of NT69L, a brain-permeable NT analog, increased ethanol sensitivity in wild-type littermates but had no such effect in NTS1 null mice, suggesting that NTS1 contributes to NT-mediated ethanol intoxication. Furthermore, the daily treatment of NT69L, for 4 consecutive days, significantly reduced alcohol preference and consumption in wild-type littermates but had no such effects in NTS1 null mice in a two-bottle drinking experiment. Our study provides evidence for possible pharmacological roles of NT69L in which it increases sensitivity to the ataxic effect, and decreases voluntary consumption, of ethanol. Our study also demonstrates NTS1-mediated behavioral effects of NT69L. Therefore, our findings will be useful for understanding some aspects of alcoholism as well as to develop novel pharmacological therapeutic options for humans.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Banbury Conference on Genetic Background in Mice. Mutant Mice and Neuroscience: Recommendations Concerning Genetic Background. Neuron. 1997;19:755–759. - PubMed
-
- Boudin H, Pelaprat D, Rostene W, Beaudet A. Cellular distribution of neurotensin receptors in rat brain: immunohistochemical study using an antipeptide antibody against the cloned high affinity receptor. J Comp Neurol. 1996;373:76–89. - PubMed
-
- Boules M, Fredrickson P, Richelson E. Bioactive analogs of neurotensin: focus on CNS effects. Peptides. 2006;27:2523–2533. - PubMed
-
- Boules M, Fredrickson P, Richelson E. Neurotensin agonists as an alternative to antipsychotics. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2005;14:359–369. - PubMed
-
- Caceda R, Kinkead B, Nemeroff CB. Neurotensin: role in psychiatric and neurological diseases. Peptides. 2006;27:2385–2404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

