Transcriptional regulation by HMGN proteins
- PMID: 20123070
- PMCID: PMC2818479
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2009.11.006
Transcriptional regulation by HMGN proteins
Abstract
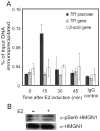
High mobility group nucleosomal proteins (HMGNs) are small non-histone proteins associated with chromatin. HMGNs have the unique ability to bind to nucleosomes with higher affinity than to naked DNA [1]. They have been studied extensively for their ability to modulate transcription. Although initially viewed as general transcriptional activators on chromatin templates, it is now appreciated that they are instead highly specific modulators of gene expression. We review the mechanisms for targeting HMGNs to specific genes and for how they subsequently regulate transcription.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bustin M, Reeves R. High-mobility-group chromosomal proteins: architectural components that facilitate chromatin function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1996;54:35–100. - PubMed
-
- Kootstra A. Isolation of high mobility group-containing mononucleosomes from avian erythrocyte nuclei and their sensitivity to DNase I. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:13088–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

