Infection with AV-SUR2A protects H9C2 cells against metabolic stress: a mechanism of SUR2A-mediated cytoprotection independent from the K(ATP) channel activity
- PMID: 20123112
- PMCID: PMC2881534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.01.018
Infection with AV-SUR2A protects H9C2 cells against metabolic stress: a mechanism of SUR2A-mediated cytoprotection independent from the K(ATP) channel activity
Abstract
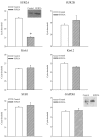
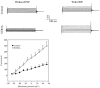
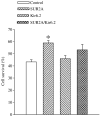
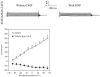
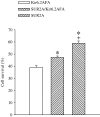
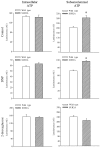
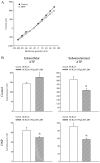
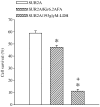
Transgenic mice overexpressing SUR2A, a subunit of ATP-sensitive K(+) (K(ATP)) channels, acquire resistance to myocardial ischaemia. However, the mechanism of SUR2A-mediated cytoprotection is yet to be fully understood. Adenoviral SUR2A construct (AV-SUR2A) increased SUR2A expression, number of K(ATP) channels and subsarcolemmal ATP in glycolysis-sensitive manner in H9C2 cells. It also increased K(+) current in response to chemical hypoxia, partially preserved subsarcolemmal ATP and increased cell survival. Kir6.2AFA, a mutant form of Kir6.2 with largely decreased K(+) conductance, abolished the effect of SUR2A on K(+) current, did not affect SUR2A-induced increase in subsarcolemmal ATP and partially inhibited SUR2A-mediated cytoprotection. Infection with 193gly-M-LDH, an inactive mutant of muscle lactate dehydrogenase, abolished the effect of SUR2A on K(+) current, subsarcolemmal ATP and cell survival; the effect of 193gly-M-LDH on cell survival was significantly more pronounced than those of Kir6.2AFA. We conclude that AV-SUR2A increases resistance to metabolic stress in H9C2 cells by increasing the number of sarcolemmal K(ATP) channels and subsarcolemmal ATP.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Zingman L.V., Alekseev A.E., Hodgson-Zingman D., Terzic A. ATP-sensitive K+ channels: metabolic sensing and cardioprotection. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007;103:1888–1893. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S18744/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 059528/Z/99/Z/JMW/CP/JF/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- PG/08/106/26155/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G0400608/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- PG/06/082/21196/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

