Vocalization toward conspecifics in silver foxes (Vulpes vulpes) selected for tame or aggressive behavior toward humans
- PMID: 20123117
- PMCID: PMC2873138
- DOI: 10.1016/j.beproc.2010.01.021
Vocalization toward conspecifics in silver foxes (Vulpes vulpes) selected for tame or aggressive behavior toward humans
Abstract
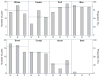
We examined the production of different vocalizations in three strains of silver fox (unselected, aggressive, and tame) attending three kinds of behavior (aggressive, affiliative, and neutral) in response to their same-strain conspecifics. This is a follow-up to previous experiments which demonstrated that in the presence of humans, tame foxes produced cackles and pants but never coughed or snorted, whilst aggressive foxes produced coughs and snorts but never cackled or panted. Thus, cackle/pant and cough/snort were indicative of the tame and aggressive fox strains respectively toward humans. Wild-type unselected foxes produced cough and snort toward humans similarly to aggressive foxes. Here, we found that vocal responses to conspecifics were similar in tame, aggressive and unselected fox strains. Both cackle/pant and cough/snort occurred in foxes of all strains. The difference in the use of cackle/pant and cough/snort among these strains toward humans and toward conspecifics suggest that silver foxes do not perceive humans as their conspecifics. We speculate that these vocalizations are produced in response to a triggering internal state, affiliative or aggressive, that is suppressed by default in these fox strains toward humans as a result of their strict selection for tame or aggressive behavior, whilst still remaining flexible toward conspecifics.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Explosive vocal activity for attracting human attention is related to domestication in silver fox.Behav Processes. 2011 Feb;86(2):216-21. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2010.12.001. Epub 2010 Dec 9. Behav Processes. 2011. PMID: 21145949 Free PMC article.
-
Kind granddaughters of angry grandmothers: the effect of domestication on vocalization in cross-bred silver foxes.Behav Processes. 2009 Jul;81(3):369-75. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2009.03.012. Behav Processes. 2009. PMID: 19520236 Free PMC article.
-
Genotyping-By-Sequencing (GBS) Detects Genetic Structure and Confirms Behavioral QTL in Tame and Aggressive Foxes (Vulpes vulpes).PLoS One. 2015 Jun 10;10(6):e0127013. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127013. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26061395 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic responses to selection for tame/aggressive behaviors in the silver fox (Vulpes vulpes).Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Oct 9;115(41):10398-10403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1800889115. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30228118 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of behavior in the silver fox.Mamm Genome. 2012 Feb;23(1-2):164-77. doi: 10.1007/s00335-011-9373-z. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Mamm Genome. 2012. PMID: 22108806 Review.
Cited by
-
Explosive vocal activity for attracting human attention is related to domestication in silver fox.Behav Processes. 2011 Feb;86(2):216-21. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2010.12.001. Epub 2010 Dec 9. Behav Processes. 2011. PMID: 21145949 Free PMC article.
-
Domestication effects on crowing in chickens: variation between wild and captive red junglefowl and domestic white Leghorn and the genetic architecture of crowing vocalizations.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025 May;380(1926):20240199. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2024.0199. Epub 2025 May 15. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40370017 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of selection for behavior, human approach mode and sex on vocalization in silver fox.J Ethol. 2013 Jan 1;31(1):95-100. doi: 10.1007/s10164-012-0353-x. Epub 2012 Nov 3. J Ethol. 2013. PMID: 23525128 Free PMC article.
-
Humans identify negative (but not positive) arousal in silver fox vocalizations: implications for the adaptive value of interspecific eavesdropping.Curr Zool. 2017 Aug;63(4):445-456. doi: 10.1093/cz/zox035. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Curr Zool. 2017. PMID: 29492004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belyaev DK. Destabilizing selection as a factor in domestication. J Hered. 1979;70:301–308. - PubMed
-
- Blumstein DT, Armitage KB. Alarm calling in yellow-bellied marmots: I. The meaning of situationally specific calls. Anim Behav. 1997;53:143–171.
-
- Cohen JA, Fox MW. Vocalizations in wild canids and possible effects of domestication. Behav Process. 1976;1:77–92. - PubMed
-
- Darden SK, Dabelsteen T. Ontogeny of swift fox Vulpes velox vocalizations: production, usage and response. Behaviour. 2006;143:659–681.
-
- Dujardin E, Jürgens U. Call type-specific differences in vocalization-related afferents to the periaqueductal gray of squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus) Behav Brain Res. 2006;168:23–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

