Preparation of a highly active cell-free translation system from immature Xenopus laevis oocytes
- PMID: 20123127
- PMCID: PMC2868112
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2010.01.031
Preparation of a highly active cell-free translation system from immature Xenopus laevis oocytes
Abstract
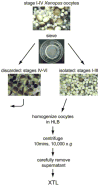
Understanding mechanisms of post-transcriptional control of gene expression has come under much scrutiny in recent years. A key question in this field is how the translation of specific mRNAs is activated or repressed both spatially and temporally in a given cell. In oocytes of the frog Xenopus laevis a number of mRNAs are localized early in oogenesis and subsequently translated at later stages. We have developed a highly active cell-free translation system from oocytes in the early stages of oogenesis that is applicable to the study of translation and translational control of both endogenous and exogenous mRNAs.
Figures
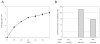

Similar articles
-
Xenopus laevis zygote arrest 2 (zar2) encodes a zinc finger RNA-binding protein that binds to the translational control sequence in the maternal Wee1 mRNA and regulates translation.Dev Biol. 2012 Sep 15;369(2):177-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.06.012. Epub 2012 Jun 23. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22732570 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and pathway of Luciola mingrelica firefly luciferase in Xenopus laevis frog oocytes and in cell-free systems.Biochimie. 1989 Apr;71(4):579-83. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(89)90190-9. Biochimie. 1989. PMID: 2503063
-
Zar1 represses translation in Xenopus oocytes and binds to the TCS in maternal mRNAs with different characteristics than Zar2.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1829(10):1034-46. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23827238 Free PMC article.
-
Controlling the Messenger: Regulated Translation of Maternal mRNAs in Xenopus laevis Development.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;953:49-82. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46095-6_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 27975270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of translational control in early development.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996 Oct;6(5):555-61. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(96)80083-9. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996. PMID: 8939728 Review.
References
-
- Beckler GS, Thompson D, Van Oosbree T. In vitro translation using rabbit reticulocyte lysate. Methods Mol Biol. 1995;37:215–32. - PubMed
-
- Castagnetti S, Hentze MW, Ephrussi A, Gebauer F. Control of oskar mRNA translation by Bruno in a novel cell-free system from Drosophila ovaries. Development. 2000;127:1063–8. - PubMed
-
- Van Herwynen JF, Beckler GS. Translation using a wheat-germ extract. Methods Mol Biol. 1995;37:245–51. - PubMed
-
- Acker MG, Kolitz SE, Mitchell SF, Nanda JS, Lorsch JR. Reconstitution of yeast translation initiation. Methods Enzymol. 2007;430:111–45. - PubMed
-
- Pisarev AV, Unbehaun A, Hellen CU, Pestova TV. Assembly and analysis of eukaryotic translation initiation complexes. Methods Enzymol. 2007;430:147–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

