Glowing in the dark: not always a bad thing
- PMID: 20123140
- PMCID: PMC2945228
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.05.065
Glowing in the dark: not always a bad thing
Figures
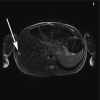
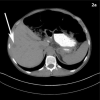


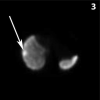
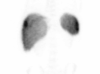
References
-
- Marin D, Brancatelli G, Federle MP, Lagalla R, Catalano C, Passariello R, Midiri M, Vilgrain V. Focal nodular hyperplasia: typical and atypical MRI findings with emphasis on the use of contrast media. Clin Radiol. 2008;63:577–85. - PubMed
-
- Herman P, Pugliese V, Machado MA, Montagnini AL, Salem MZ, Bacchella T, D'Albuquerque LA, Saad WA, Machado MC, Pinotti HW. Hepatic adenoma and focal nodular hyperplasia: differential diagnosis and treatment. World J Surg. 2000;24:372–6. - PubMed
-
- Shamsi K, De Schepper A, Degryse H, Deckers F. Focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver: radiologic findings. Abdom Imaging. 1993;18:32–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

