Expression of the BabA adhesin during experimental infection with Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 20123715
- PMCID: PMC2849406
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01297-09
Expression of the BabA adhesin during experimental infection with Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
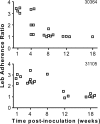
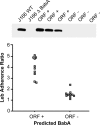
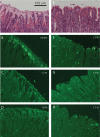
The Helicobacter pylori babA gene encodes an outer membrane protein that mediates binding to fucosylated ABH antigens of the ABO blood group. We recently demonstrated that BabA expression is lost during experimental infection of rhesus macaques with H. pylori J166. We sought to test the generality of this observation by comparison of different H. pylori strains and different animal hosts. Challenge of macaques with H. pylori J99 yielded output strains that lost BabA expression, either by selection and then expansion of a subpopulation of J99 that had a single-base-pair mutation that encoded a stop codon or by gene conversion of babA with a duplicate copy of babB, a paralog of unknown function. Challenge of mice with H. pylori J166, which unlike J99, has 5' CT repeats in babA, resulted in loss of BabA expression due to phase variation. In the gerbil, Leb binding was lost by replacement of the babA gene that encoded Leb binding with a nonbinding allele that differed at six amino acid residues. Complementation experiments confirmed that change in these six amino acids of BabA was sufficient to eliminate binding to Leb and to gastric tissue. These results demonstrate that BabA expression in vivo is highly dynamic, and the findings implicate specific amino acid residues as critical for binding to fucosylated ABH antigens. We hypothesize that modification of BabA expression during H. pylori infection is a mechanism to adapt to changing conditions of inflammation and glycan expression at the epithelial surface.
Figures
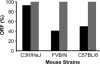

References
-
- Alm, R. A., L. L. Ling, D. T. Moir, B. L. King, E. D. Brown, P. C. Doig, D. R. Smith, B. Noonan, B. C. Guild, B. L. deJonge, G. Carmel, P. J. Tummino, A. Caruso, M. Uria-Nickelsen, D. M. Mills, C. Ives, R. Gibson, D. Merberg, S. D. Mills, Q. Jiang, D. E. Taylor, G. F. Vovis, and T. J. Trust. 1999. Genomic-sequence comparison of two unrelated isolates of the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature 397:176-180. - PubMed
-
- Aspholm-Hurtig, M., G. Dailide, M. Lahmann, A. Kalia, D. Ilver, N. Roche, S. Vikstrom, R. Sjostrom, S. Linden, A. Backstrom, C. Lundberg, A. Arnqvist, J. Mahdavi, U. J. Nilsson, B. Velapatino, R. H. Gilman, M. Gerhard, T. Alarcon, M. Lopez-Brea, T. Nakazawa, J. G. Fox, P. Correa, M. G. Dominguez-Bello, G. I. Perez-Perez, M. J. Blaser, S. Normark, I. Carlstedt, S. Oscarson, S. Teneberg, D. E. Berg, and T. Boren. 2004. Functional adaptation of BabA, the H. pylori ABO blood group antigen binding adhesin. Science 305:519-522. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1990. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 AI070803/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI60555/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI060555/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R29 CA077955/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK063041/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA116087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA116087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI42081/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058587/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK58587/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI042081/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA077955/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK63041/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA77955/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI070803/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

