Comparison of the 'Denver regimen' against acute tuberculosis in the mouse and guinea pig
- PMID: 20123722
- PMCID: PMC2837551
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkq007
Comparison of the 'Denver regimen' against acute tuberculosis in the mouse and guinea pig
Abstract
Objectives: In this study, we sought to compare the sterilizing activity of human-equivalent doses of the 'Denver regimen' against acute tuberculosis (TB) infection in the standard mouse model and in the guinea pig.
Methods: Pharmacokinetic studies in guinea pigs were used to establish human-equivalent doses for rifampicin, isoniazid and pyrazinamide. Guinea pigs and mice were aerosol-infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis CDC1551 and treatment was started 2 weeks later with rifampicin/isoniazid/pyrazinamide for up to 6 months. For the first 2 weeks of therapy, the dosing frequency was 5 days/week, and for the remaining period, twice weekly. Treatment was discontinued in groups of 30 mice and 10 guinea pigs at 5 months and at 6 months, and these animals were held for a further 3 months in order to assess relapse rates.
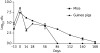
Results: Guinea pig lungs became culture-negative after 3 months of predominantly twice-weekly treatment and relapse rates were 0% (0/10) both after 5 months and after 6 months of treatment. In contrast, all mice remained culture-positive despite 6 months of the same treatment, and 93% (28/30) and 69% (20/29) of mice relapsed after treatment for 5 and 6 months, respectively.
Conclusions: Treatment with rifampicin/isoniazid/pyrazinamide administered at human-equivalent doses is much more potent against acute TB infection in guinea pigs than in mice. Our findings have important implications for the use of alternative animal models in testing novel TB drug regimens and for modelling M. tuberculosis persistence.
Figures
References
-
- Nuermberger E. Using animal models to develop new treatments for tuberculosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;29:542–51. - PubMed
-
- Schatz A, Bugie E, Waksman SA. Streptomycin, a substance exhibiting antibiotic activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1944;55:66–9. - PubMed
-
- McCune RM, Jr, McDermott W, Tompsett R. The fate of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mouse tissues as determined by the microbial enumeration technique. II. The conversion of tuberculous infection to the latent state by the administration of pyrazinamide and a companion drug. J Exp Med. 1956;104:763–802. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nuermberger EL, Yoshimatsu T, Tyagi S, et al. Moxifloxacin-containing regimen greatly reduces time to culture conversion in murine tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;169:421–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

