Translational control analysis by translationally active RNA capture/microarray analysis (TrIP-Chip)
- PMID: 20123731
- PMCID: PMC2875024
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq024
Translational control analysis by translationally active RNA capture/microarray analysis (TrIP-Chip)
Abstract
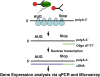
We have developed a new approach to systematically study post-transcriptional regulation in a small number of cells. Actively translating mRNAs are associated with polysomes and the newly synthesized peptide chains are closely associated with molecular chaperones such as hsp70s, which assist in the proper folding of nascent polypeptides into higher ordered structures. These chaperones provide an anchor with which to separate actively translating mRNAs associated with polysomes from free mRNAs. Affinity capture beads were developed to capture hsp70 chaperones associated with the polysome complexes. The isolated actively translating mRNAs were used for high-throughput expression profiling analysis. Feasibility was demonstrated using an in vitro translation system with known translationally regulated mRNA transcript thymidylate synthase (TS). We further developed the approach using HCT-116 colon cancer cells with both TS and p53 as positive controls. The steady-state levels of TS and p53 mRNAs were unaltered after 5-fluorouracil treatment as assessed by real-time qRT-PCR analysis. In contrast, the protein expression and polysome-associated mRNA levels of both genes were increased. These differences in translational rate were revealed with our new approach from 500 cells. This technology has the potential to make investigation of translational control feasible with limited quantities of clinical specimens.
Figures


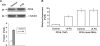
Similar articles
-
Identification of miR-215 mediated targets/pathways via translational immunoprecipitation expression analysis (TrIP-chip).Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 15;6(27):24463-73. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4425. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26287603 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-level gene expression profiles affected by thymidylate synthase and 5-fluorouracil in colon cancer.BMC Genomics. 2006 Apr 3;7:68. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-68. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16584549 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profiling reveals meiotic male germ cell mRNAs that are translationally up- and down-regulated.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 16;103(20):7712-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510999103. Epub 2006 May 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16682651 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of mRNA polysomal profiles with spotted DNA microarrays.Methods Enzymol. 2007;431:177-201. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)31010-0. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17923236 Review.
-
Signal transduction: putting translation before transcription.Cancer Cell. 2003 Oct;4(4):244-5. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00247-2. Cancer Cell. 2003. PMID: 14585349 Review.
Cited by
-
Staufen1 promotes HCV replication by inhibiting protein kinase R and transporting viral RNA to the site of translation and replication in the cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jun 20;44(11):5271-87. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw312. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27106056 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation and function of 5'-untranslated GR-exon 1 transcripts.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Jul;25(7):1100-10. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0436. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21527501 Free PMC article.
-
The chemotherapeutic drug 5-fluorouracil promotes PKR-mediated apoptosis in a p53-independent manner in colon and breast cancer cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23887. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023887. Epub 2011 Aug 24. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21887339 Free PMC article.
-
Translational reprogramming of colorectal cancer cells induced by 5-fluorouracil through a miRNA-dependent mechanism.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 11;8(28):46219-46233. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17597. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28515355 Free PMC article.
-
The gene-specific codon counting database: a genome-based catalog of one-, two-, three-, four- and five-codon combinations present in Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes.Database (Oxford). 2012 Feb 8;2012:bas002. doi: 10.1093/database/bas002. Print 2012. Database (Oxford). 2012. PMID: 22323063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chu E, Allegra CJ. The role of thymidylate synthase as an RNA binding protein. Bioessays. 1996;18:191–198. - PubMed
-
- Mikulits W, Pradet-Balade B, Habermann B, Beug H, Garcia-Sanz JA, Mullner EW. Isolation of translationally controlled mRNAs by differential screening. FASEB J. 2000;14:1641–1652. - PubMed
-
- Derrigo M, Cestelli A, Savettieri G, Di Liegro I. RNA-protein interactions in the control of stability and localization of messenger RNA (review) Int. J. Mol. Med. 2000;5:111–123. - PubMed
-
- Sheikh MS, Fornace A.J., Jr Regulation of translation initiation following stress. Oncogene. 1999;18:6121–6128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

