Gravitational lensing: a unique probe of dark matter and dark energy
- PMID: 20123743
- PMCID: PMC3263800
- DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2009.0209
Gravitational lensing: a unique probe of dark matter and dark energy
Abstract
I review the development of gravitational lensing as a powerful tool of the observational cosmologist. After the historic eclipse expedition organized by Arthur Eddington and Frank Dyson, the subject lay observationally dormant for 60 years. However, subsequent progress has been astonishingly rapid, especially in the past decade, so that gravitational lensing now holds the key to unravelling the two most profound mysteries of our Universe-the nature and distribution of dark matter, and the origin of the puzzling cosmic acceleration first identified in the late 1990s. In this non-specialist review, I focus on the unusual history and achievements of gravitational lensing and its future observational prospects.
Figures


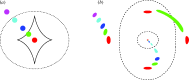
 derived from a combination of the lensing geometry and stellar dynamics of the lensing elliptical. The remarkable uniformity in the mass profile argues for early formation concurrent with the assembly of a massive dark matter halo.
derived from a combination of the lensing geometry and stellar dynamics of the lensing elliptical. The remarkable uniformity in the mass profile argues for early formation concurrent with the assembly of a massive dark matter halo.



Similar articles
-
Gravitational Lensing in Astronomy.Living Rev Relativ. 1998;1(1):12. doi: 10.12942/lrr-1998-12. Epub 1998 Nov 2. Living Rev Relativ. 1998. PMID: 28937183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bending space-time: a commentary on Dyson, Eddington and Davidson (1920) 'A determination of the deflection of light by the Sun's gravitational field'.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2015 Apr 13;373(2039):20140287. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2014.0287. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2015. PMID: 25750149 Free PMC article.
-
Cosmology with cosmic shear observations: a review.Rep Prog Phys. 2015 Jul;78(8):086901. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/78/8/086901. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Rep Prog Phys. 2015. PMID: 26181770 Review.
-
Cosmology with weak lensing surveys.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2005 Dec 15;363(1837):2675-91. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2005.1672. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2005. PMID: 16286284 Review.
-
Introduction.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2003 Nov 15;361(1812):2427-34. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2003.1289. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2003. PMID: 14667310
Cited by
-
Automation of finding strong gravitational lenses in the Kilo Degree Survey with U - DenseLens (DenseLens + Segmentation).Mon Not R Astron Soc. 2024 Aug 6;533(2):1426-1441. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stae1882. eCollection 2024 Sep. Mon Not R Astron Soc. 2024. PMID: 39176180 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of a new type of Dark Matter with the Milky Way and M31 grand rotation curves.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 15;14(1):24090. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74884-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39406824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alcock C., et al. Possible gravitational microlensing of a star in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Nature. 1993;365:621–623. doi: 10.1038/365621a0. ( ) - DOI
-
- Astier P., et al. The Supernova Legacy Survey: measurement of ΩM, ΩΛ and w from the first year data set. Astron. Astrophys. 2006;447:31–48. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361:20054185. ( ) - DOI
-
- Aubourg E., et al. Evidence for gravitational microlensing by dark objects in the Galactic halo. Nature. 1993;365:623–625. doi: 10.1038/365623a0. ( ) - DOI
-
- Bacon D., Refregier A., Ellis R. S. Detection of weak gravitational lensing by large-scale structure. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2000;318:625–640. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-8711.2000.03851.x. ( ) - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

