Prefrontal-enriched SLIT1 expression in Old World monkey cortex established during the postnatal development
- PMID: 20123755
- PMCID: PMC2936805
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhp319
Prefrontal-enriched SLIT1 expression in Old World monkey cortex established during the postnatal development
Abstract
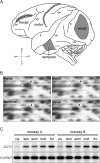
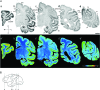
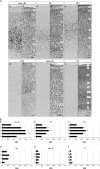
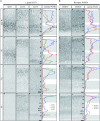
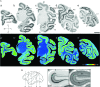
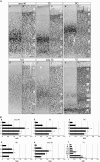
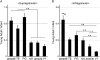
To elucidate the molecular basis of the specialization of cortical architectures, we searched for genes differentially expressed among neocortical areas of Old World monkeys by restriction landmark cDNA scanning . We found that mRNA of SLIT1, an axon guidance molecule, was enriched in the prefrontal cortex but with developmentally related changes. In situ hybridization analysis revealed that SLIT1 mRNA was mainly distributed in the middle layers of most cortical areas, robustly in the prefrontal cortex and faintly in primary sensory areas. The lowest expression was in the primary visual area. Analyses of other SLIT (SLIT2 and SLIT3) mRNAs showed preferential expression in the prefrontal cortex with a distinct laminar pattern. By contrast, the receptor Roundabout (ROBO1 and ROBO2) mRNAs were widely distributed throughout the cortex. Perinatally, SLIT1 mRNA was abundantly expressed in the cortex with modest area specificity. Downregulation of expression initially occurred in early sensory areas around postnatal day 60 and followed in the association areas. The prefrontal area-enriched SLIT1 mRNA expression results from a relatively greater attenuation of this expression in the other areas. These results suggest that its role is altered postnatally and that this is particularly important for prefrontal connectivity in the Old World monkey cortex.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression patterns of SLIT/ROBO mRNAs reveal a characteristic feature in the entorhinal-hippocampal area of macaque monkeys.BMC Res Notes. 2020 May 27;13(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s13104-020-05100-7. BMC Res Notes. 2020. PMID: 32460877 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the vertebrate Slit gene family and their putative receptors, the Robo genes, in the developing murine kidney.Mech Dev. 2000 Jun;94(1-2):213-7. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(00)00313-0. Mech Dev. 2000. PMID: 10842075
-
Spatiotemporal expression patterns of slit and robo genes in the rat brain.J Comp Neurol. 2002 Jan 7;442(2):130-55. doi: 10.1002/cne.10068. J Comp Neurol. 2002. PMID: 11754167
-
Dynamic changes in Robo2 and Slit1 expression in adult rat dorsal root ganglion and sciatic nerve after peripheral and central axonal injury.Neurosci Res. 2006 Nov;56(3):314-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2006.07.014. Epub 2006 Sep 18. Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16979769
-
Slits and their receptors.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;621:65-80. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-76715-4_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 18269211 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of viral vectors to the study of neural connectivities and neural circuits in the marmoset brain.Dev Neurobiol. 2017 Mar;77(3):354-372. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22459. Epub 2016 Oct 26. Dev Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27706918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vivo Two-Photon Imaging of Dendritic Spines in Marmoset Neocortex.eNeuro. 2015 Sep 17;2(4):ENEURO.0019-15.2015. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0019-15.2015. eCollection 2015 Jul-Aug. eNeuro. 2015. PMID: 26465000 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Axon Guidance: Roles of Slit-Robo Signaling in Neocortical Formation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Dec 23;8:607415. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.607415. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33425915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Convergent transcriptional specializations in the brains of humans and song-learning birds.Science. 2014 Dec 12;346(6215):1256846. doi: 10.1126/science.1256846. Science. 2014. PMID: 25504733 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation and methyl-binding proteins control differential gene expression in distinct cortical areas of macaque monkey.J Neurosci. 2013 Dec 11;33(50):19704-14. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2355-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24336734 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrews W, Liapi A, Plachez C, Camurri L, Zhang J, Mori S, Murakami F, Parnavelas JG, Sundaresan V, Richards LJ. Robo1 regulates the development of major axon tracts and interneuron migration in the forebrain. Development. 2006;133:2243–2252. - PubMed
-
- Annese J, Gazzaniga MS, Toga AW. Localization of the human cortical visual area MT based on computer aided histological analysis. Cereb Cortex. 2005;15:1044–1053. - PubMed
-
- Bagri A, Marin O, Plump AS, Mak J, Pleasure SJ, Rubenstein JL, Tessier-Lavigne M. Slit proteins prevent midline crossing and determine the dorsoventral position of major axonal pathways in the mammalian forebrain. Neuron. 2002;33:233–248. - PubMed
-
- Bahi A, Dreyer JL. Cocaine-induced expression changes of axon guidance molecules in the adult rat brain. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005;28:275–291. - PubMed

