Autoantibodies against IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 in patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis and autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I
- PMID: 20123958
- PMCID: PMC2822614
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20091983
Autoantibodies against IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 in patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis and autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I
Abstract
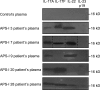
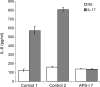
Most patients with autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I (APS-I) display chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis (CMC). We hypothesized that this CMC might result from autoimmunity to interleukin (IL)-17 cytokines. We found high titers of autoantibodies (auto-Abs) against IL-17A, IL-17F, and/or IL-22 in the sera of all 33 patients tested, as detected by multiplex particle-based flow cytometry. The auto-Abs against IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 were specific in the five patients tested, as shown by Western blotting. The auto-Abs against IL-17A were neutralizing in the only patient tested, as shown by bioassays of IL-17A activity. None of the 37 healthy controls and none of the 103 patients with other autoimmune disorders tested had such auto-Abs. None of the patients with APS-I had auto-Abs against cytokines previously shown to cause other well-defined clinical syndromes in other patients (IL-6, interferon [IFN]-gamma, or granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor) or against other cytokines (IL-1beta, IL-10, IL-12, IL-18, IL-21, IL-23, IL-26, IFN-beta, tumor necrosis factor [alpha], or transforming growth factor beta). These findings suggest that auto-Abs against IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 may cause CMC in patients with APS-I.
Figures

Comment in
-
Antibodies attack IL-17.J Exp Med. 2010 Feb 15;207(2):264-5. doi: 10.1084/jem.2072iti3. Epub 2010 Feb 1. J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 20123956 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- de Beaucoudrey L., Puel A., Filipe-Santos O., Cobat A., Ghandil P., Chrabieh M., Feinberg J., von Bernuth H., Samarina A., Jannière L., et al. 2008. Mutations in STAT3 and IL12RB1 impair the development of human IL-17–producing T cells. J. Exp. Med. 205:1543–1550 10.1084/jem.20080321 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

