The motor protein myosin-X transports VE-cadherin along filopodia to allow the formation of early endothelial cell-cell contacts
- PMID: 20123970
- PMCID: PMC2838073
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01226-09
The motor protein myosin-X transports VE-cadherin along filopodia to allow the formation of early endothelial cell-cell contacts
Abstract
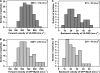
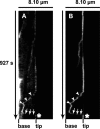
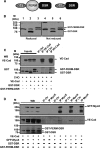
Vascular endothelium (VE), the monolayer of endothelial cells that lines the vascular tree, undergoes damage at the basis of some vascular diseases. Its integrity is maintained by VE-cadherin, an adhesive receptor localized at cell-cell junctions. Here, we show that VE-cadherin is also located at the tip and along filopodia in sparse or subconfluent endothelial cells. We observed that VE-cadherin navigates along intrafilopodial actin filaments. We found that the actin motor protein myosin-X is colocalized and moves synchronously with filopodial VE-cadherin. Immunoprecipitation and pulldown assays confirmed that myosin-X is directly associated with the VE-cadherin complex. Furthermore, expression of a dominant-negative mutant of myosin-X revealed that myosin-X is required for VE-cadherin export to cell edges and filopodia. These features indicate that myosin-X establishes a link between the actin cytoskeleton and VE-cadherin, thereby allowing VE-cadherin transportation along intrafilopodial actin cables. In conclusion, we propose that VE-cadherin trafficking along filopodia using myosin-X motor protein is a prerequisite for cell-cell junction formation. This mechanism may have functional consequences for endothelium repair in pathological settings.
Figures









References
-
- Berg, J. S., and R. E. Cheney. 2002. Myosin-X is an unconventional myosin that undergoes intrafilopodial motility. Nat. Cell Biol. 4:246-250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
