Mutual regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase and the mitotic exit network
- PMID: 20123997
- PMCID: PMC2819678
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200911128
Mutual regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase and the mitotic exit network
Abstract
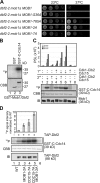
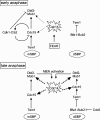
The mitotic exit network (MEN) is a spindle pole body (SPB)-associated, GTPase-driven signaling cascade that controls mitotic exit. The inhibitory Bfa1-Bub2 GTPase-activating protein (GAP) only associates with the daughter SPB (dSPB), raising the question as to how the MEN is regulated on the mother SPB (mSPB). Here, we show mutual regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1) and the MEN. In early anaphase Cdk1 becomes recruited to the mSPB depending on the activity of the MEN kinase Cdc15. Conversely, Cdk1 negatively regulates binding of Cdc15 to the mSPB. In addition, Cdk1 phosphorylates the Mob1 protein to inhibit the activity of Dbf2-Mob1 kinase that regulates Cdc14 phosphatase. Our data revise the understanding of the spatial regulation of the MEN. Although MEN activity in the daughter cells is controlled by Bfa1-Bub2, Cdk1 inhibits MEN activity at the mSPB. Consistent with this model, only triple mutants that lack BUB2 and the Cdk1 phosphorylation sites in Mob1 and Cdc15 show mitotic exit defects.
Figures







References
-
- Bailly E., Cabantous S., Sondaz D., Bernadac A., Simon M.N. 2003. Differential cellular localization among mitotic cyclins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a new role for the axial budding protein Bud3 in targeting Clb2 to the mother-bud neck. J. Cell Sci. 116:4119–4130 10.1242/jcs.00706 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

