Quantitative and qualitative alterations of heparan sulfate in fibrogenic liver diseases and hepatocellular cancer
- PMID: 20124094
- PMCID: PMC2857815
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.2010.955161
Quantitative and qualitative alterations of heparan sulfate in fibrogenic liver diseases and hepatocellular cancer
Abstract
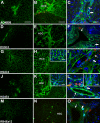
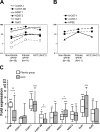
Heparan sulfate (HS), due to its ability to interact with a multitude of HS-binding factors, is involved in a variety of physiological and pathological processes. Remarkably diverse fine structure of HS, shaped by non-exhaustive enzymatic modifications, influences the interaction of HS with its partners. Here we characterized the HS profile of normal human and rat liver, as well as alterations of HS related to liver fibrogenesis and carcinogenesis, by using sulfation-specific antibodies. The HS immunopattern was compared with the immunolocalization of selected HS proteoglycans. HS samples from normal liver and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) were subjected to disaccharide analysis. Expression changes of nine HS-modifying enzymes in human fibrogenic diseases and HCC were measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Increased abundance and altered immunolocalization of HS was paralleled by elevated mRNA levels of HS-modifying enzymes in the diseased liver. The strong immunoreactivity of the normal liver for 3-O-sulfated epitope further increased with disease, along with upregulation of 3-OST-1. Modest 6-O-undersulfation of HCC HS is probably explained by Sulf overexpression. Our results may prompt further investigation of the role of highly 3-O-sulfated and partially 6-O-desulfated HS in pathological processes such as hepatitis virus entry and aberrant growth factor signaling in fibrogenic liver diseases and HCC.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of the expression of agrin, a basement membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan, in cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma.Hum Pathol. 2007 Oct;38(10):1508-15. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2007.02.017. Epub 2007 Jul 19. Hum Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17640714
-
[Selective deposition of agrin in the microvasculature of hepatocellular carcinoma: aspects in pathogenesis and differential diagnosis].Magy Onkol. 2008 Dec;52(4):379-83. doi: 10.1556/MOnkol.52.2008.4.7. Magy Onkol. 2008. PMID: 19068466 Hungarian.
-
Overexpression of heparan sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferases in human embryonic kidney 293 cells results in increased N-acetylglucosaminyl 6-O-sulfation.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 3;281(9):5348-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509584200. Epub 2005 Dec 2. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16326709
-
[Proteoglycans in the liver].Magy Onkol. 2004;48(3):207-13. Epub 2004 Nov 1. Magy Onkol. 2004. PMID: 15520870 Review. Hungarian.
-
Proteoglycans in liver cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jan 7;22(1):379-93. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i1.379. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26755884 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional Activity of Heparan Sulfate Biosynthetic Machinery is Specifically Impaired in Benign Prostate Hyperplasia and Prostate Cancer.Front Oncol. 2014 Apr 15;4:79. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00079. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24782989 Free PMC article.
-
SULF1/SULF2 reactivation during liver damage and tumour growth.Histochem Cell Biol. 2016 Jul;146(1):85-97. doi: 10.1007/s00418-016-1425-8. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Histochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27013228
-
Potential Use of Anti-Inflammatory Synthetic Heparan Sulfate to Attenuate Liver Damage.Biomedicines. 2020 Nov 16;8(11):503. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8110503. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 33207634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased EXT1 gene copy number correlates with increased mRNA level predicts short disease-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma without vascular invasion.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Sep;97(39):e12625. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012625. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30278583 Free PMC article.
-
Global Gene Expression Profiling Reveals Isorhamnetin Induces Hepatic-Lineage Specific Differentiation in Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 5;8:578036. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.578036. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33224947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashikari-Hada S, Habuchi H, Kariya Y, Itoh N, Reddi AH, Kimata K (2004) Characterization of growth factor-binding structures in heparin/heparan sulfate using an octasaccharide library. J Biol Chem 279:12346–12354 - PubMed
-
- Barth H, Schafer C, Adah MI, Zhang F, Linhardt RJ, Toyoda H, Kinoshita-Toyoda A, et al. (2003) Cellular binding of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2 requires cell surface heparan sulfate. J Biol Chem 278:41003–41012 - PubMed
-
- Bishop JR, Schuksz M, Esko JD (2007) Heparan sulphate proteoglycans fine-tune mammalian physiology. Nature 446:1030–1037 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

