Protein aggregation in a mutant deficient in yajL, the bacterial homolog of the Parkinsonism-associated protein DJ-1
- PMID: 20124404
- PMCID: PMC2856238
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.077529
Protein aggregation in a mutant deficient in yajL, the bacterial homolog of the Parkinsonism-associated protein DJ-1
Abstract
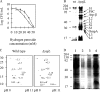
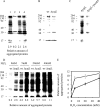
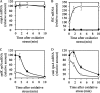
YajL is the closest prokaryotic homolog of the parkinsonism-associated protein DJ-1 (40% sequence identity and similar three-dimensional structure), a protein of unknown function involved in the cellular response to oxidative stress. We report here that a yajL mutant of Escherichia coli displays an increased sensitivity to oxidative stress. It also exhibits a protein aggregation phenotype in aerobiosis, but not in anaerobiosis or in aerobic cells overexpressing superoxide dismutase, suggesting that protein aggregation depends on the presence of reactive oxygen species produced by respiratory chains. The protein aggregation phenotype of the yajL mutant, which can be rescued by the wild-type yajL gene, but not by the corresponding cysteine 106 mutant allele, is similar to that of multiple mutants deficient in superoxide dismutases and catalases, although intracellular hydrogen peroxide levels were not increased in the yajL mutant, suggesting that protein aggregation in this strain does not result from a hydrogen peroxide detoxification defect. Aggregation-prone proteins included 17 ribosomal proteins, the ATP synthase beta subunit, flagellin, and the outer membrane proteins OmpA and PAL; all of them are part of multiprotein complexes, suggesting that YajL might be involved in optimal expression of these complexes, especially during oxidative stress. YajL stimulated the renaturation of urea-unfolded citrate synthase and the solubilization of the urea-unfolded ribosomal proteins S1 and L3 and was more efficient as a chaperone in its oxidized form than in its reduced form. The mRNA levels of several aggregated proteins of the yajL mutant were severely affected, suggesting that YajL also acts at the level of gene expression. These two functions of YajL might explain the protein aggregation phenotype of the yajL mutant.
Figures



Similar articles
-
YajL, prokaryotic homolog of parkinsonism-associated protein DJ-1, functions as a covalent chaperone for thiol proteome.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 17;287(8):5861-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.299198. Epub 2011 Dec 7. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22157000 Free PMC article.
-
Global stress response in a prokaryotic model of DJ-1-associated Parkinsonism.J Bacteriol. 2013 Mar;195(6):1167-78. doi: 10.1128/JB.02202-12. Epub 2013 Jan 4. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23292772 Free PMC article.
-
YajL, the prokaryotic homolog of the Parkinsonism-associated protein DJ-1, protects cells against protein sulfenylation.J Mol Biol. 2012 Aug 24;421(4-5):662-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.01.047. Epub 2012 Feb 1. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22321799
-
Cellular and molecular physiology of Escherichia coli in the adaptation to aerobic environments.J Biochem. 1996 Dec;120(6):1055-63. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a021519. J Biochem. 1996. PMID: 9010748 Review.
-
Regulators of oxidative stress response genes in Escherichia coli and their functional conservation in bacteria.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012 Sep 15;525(2):161-9. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.02.007. Epub 2012 Feb 20. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22381957 Review.
Cited by
-
YajL, prokaryotic homolog of parkinsonism-associated protein DJ-1, functions as a covalent chaperone for thiol proteome.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 17;287(8):5861-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.299198. Epub 2011 Dec 7. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22157000 Free PMC article.
-
Translational defects in a mutant deficient in YajL, the bacterial homolog of the parkinsonism-associated protein DJ-1.J Bacteriol. 2010 Dec;192(23):6302-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.01077-10. Epub 2010 Oct 1. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20889753 Free PMC article.
-
The cell biology of Parkinson's disease.J Cell Biol. 2021 Apr 5;220(4):e202012095. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202012095. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33749710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parkinsonism-associated protein DJ-1/Park7 is a major protein deglycase that repairs methylglyoxal- and glyoxal-glycated cysteine, arginine, and lysine residues.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 16;290(3):1885-97. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.597815. Epub 2014 Nov 21. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25416785 Free PMC article.
-
δ-Opioid Receptor Activation Attenuates the Oligomer Formation Induced by Hypoxia and/or α-Synuclein Overexpression/Mutation Through Dual Signaling Pathways.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 May;56(5):3463-3475. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1316-1. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30132200
References
-
- Malki A., Caldas T., Abdallah J., Kern R., Eckey V., Kim S. J., Cha S. S., Mori H., Richarme G. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280, 14420–14426 - PubMed
-
- Sastry M. S., Korotkov K., Brodsky Y., Baneyx F. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 46026–46034 - PubMed
-
- Cookson M. R. (2005) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 74, 29–52 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

