Thrombospondin 1--a key astrocyte-derived neurogenic factor
- PMID: 20124433
- PMCID: PMC3231793
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.09-150573
Thrombospondin 1--a key astrocyte-derived neurogenic factor
Abstract
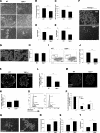
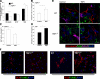
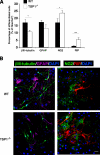
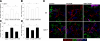
Thrombospondin 1 (TSP1), an oligomeric matrix protein, is known for its antiangiogenic activity. Recently, TSP1 has been shown to regulate synaptogenesis in the developing brain. In this study, we examine another role of TSP1 in the CNS, namely, in proliferation and differentiation of neural progenitor cells (NPCs). We found that adult mice deficient in TSP1 exhibit reduced proliferation of NPCs in vivo [13,330+/-826 vs. 4914+/-455 (mean+/-se wt vs. TSP1(-/-)); P<0.001, Student's t test] and impaired neuronal differentiation (1382+/-83 vs. 879+/-79; P<0.001). In vitro, NPC obtained from adult TSP1(-/-) mice display decreased proliferation in BrdU assay (48+/-8 vs. 24+/-3.5%; P<0.01) and decreased neuronal fate commitment (8+/-0.85 vs. 4.6+/-0.5%; P<0.05) in contrast to wild-type NPCs. Both proliferation and neuronal differentiation deficits are remediable in vitro by exogenous TSP1. Notably, conditioned medium from TSP1(-/-) astrocytes, unlike that from control astrocytes, fails to promote neurogenesis in wild-type NPCs, suggesting that TSP1 is one of the key molecules responsible for astrocyte-induced neurogenesis. Our data demonstrate that TSP1 is a critical participant in maintenance of the adult NPC pool and in neuronal differentiation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Increased proliferation and gliogenesis of cultured rat neural progenitor cells by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated astrocytes.Neuroimmunomodulation. 2009;16(6):365-76. doi: 10.1159/000228911. Epub 2009 Jul 17. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2009. PMID: 19609085
-
Cell autonomous and noncell-autonomous role of NF-κB p50 in astrocyte-mediated fate specification of adult neural progenitor cells.Glia. 2017 Jan;65(1):169-181. doi: 10.1002/glia.23085. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Glia. 2017. PMID: 27758000
-
TGF-beta signalling in the adult neurogenic niche promotes stem cell quiescence as well as generation of new neurons.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 Jul;18(7):1444-59. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12298. Epub 2014 Apr 30. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24779367 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombospondin 1, thrombospondin 2 and the eye.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2006 Jan;25(1):1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2005.05.001. Epub 2005 Jun 29. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2006. PMID: 15996506 Review.
-
Discovering novel phenotype-selective neurotrophic factors to treat neurodegenerative diseases.Prog Brain Res. 2004;146:168-83. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(03)46012-3. Prog Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 14699964 Review.
Cited by
-
Astrocyte-derived interleukin-6 promotes specific neuronal differentiation of neural progenitor cells from adult hippocampus.J Neurosci Res. 2010 Oct;88(13):2798-809. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22447. J Neurosci Res. 2010. PMID: 20568291 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study of the effects of concentrated growth factors in two different forms on osteogenesis in vitro.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Aug;20(2):1039-1048. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10313. Epub 2019 May 30. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31173196 Free PMC article.
-
hiPSC-derived neural stem cells from patients with schizophrenia induce an impaired angiogenesis.Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Feb 22;8(1):48. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0095-9. Transl Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29467462 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Matricellular Proteins in Disorders of the Central Nervous System.Neurochem Res. 2017 Mar;42(3):858-875. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2088-5. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 27878658 Review.
-
Novel insights into the role of NF-κB p50 in astrocyte-mediated fate specification of adult neural progenitor cells.Neural Regen Res. 2017 Mar;12(3):354-357. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.202919. Neural Regen Res. 2017. PMID: 28469638 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eriksson P. S., Perfilieva E., Bjork-Eriksson T., Alborn A. M., Nordborg C., Peterson D. A., Gage F. H. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med. 1998;4:1313–1317. - PubMed
-
- Zhao C., Deng W., Gage F. H. Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell. 2008;132:645–660. - PubMed
-
- Kempermann G., Kuhn H. G., Gage F. H. More hippocampal neurons in adult mice living in an enriched environment. Nature. 1997;386:493–495. - PubMed
-
- Ziv Y., Ron N., Butovsky O., Landa G., Sudai E., Greenberg N., Cohen H., Kipnis J., Schwartz M. Immune cells contribute to the maintenance of neurogenesis and spatial learning abilities in adulthood. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:268–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

