Aurora kinase inhibitors--rising stars in cancer therapeutics?
- PMID: 20124450
- PMCID: PMC2820587
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0765
Aurora kinase inhibitors--rising stars in cancer therapeutics?
Abstract
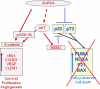
Standard therapeutic approaches of cytotoxics and radiation in cancer are not only highly toxic, but also of limited efficacy in treatment of a significant number of cancer patients. The molecular analysis of the cancer genomes have shown a remarkable complexity and pointed to key genomic and epigenomic alterations in cancer. These discoveries are paving the way for targeted therapy approaches. However, although there are a large number of potential targets, only a few can regulate key cellular functions and intersect multiple signaling networks. The Aurora kinase family members (A, B, and C) are a collection of highly related and conserved serine-threonine kinases that fulfill these criteria, being key regulators of mitosis and multiple signaling pathways. Alterations in Aurora kinase signaling are associated with mitotic errors and have been closely linked to chromosomal aneuploidy in cancer cells. Several studies have shown amplification and/or overexpression of Aurora kinase A and B in hematologic malignancies and solid tumors. Over the past several years, Aurora kinases have become attractive targets. Several ongoing clinical trials and bench-based research are assessing the unique therapeutic potential of Aurora-based targeted therapy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Aurora kinase inhibitors as anticancer molecules.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Oct-Dec;1799(10-12):829-39. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.09.004. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20863917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on aurora kinase inhibitors in gynecologic malignancies.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2008 Nov;3(3):162-77. doi: 10.2174/157489208786242322. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2008. PMID: 18991785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aurora kinases as anticancer drug targets.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Mar 15;14(6):1639-48. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-2179. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18347165 Review.
-
Aurora A kinase (AURKA) in normal and pathological cell division.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Feb;70(4):661-87. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1073-7. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22864622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aurora kinases: new targets for cancer therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Dec 1;12(23):6869-75. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1405. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17145803 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of o-chlorophenyl substituted pyrimidines as exceptionally potent aurora kinase inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2012 Sep 13;55(17):7392-7416. doi: 10.1021/jm300334d. Epub 2012 Aug 30. J Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22803810 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor activity of a small-molecule inhibitor of the histone kinase Haspin.Oncogene. 2012 Mar 15;31(11):1408-18. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.335. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 21804608 Free PMC article.
-
An exploratory phase 2 study of investigational Aurora A kinase inhibitor alisertib (MLN8237) in acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes.Leuk Res Rep. 2014 Jul 5;3(2):58-61. doi: 10.1016/j.lrr.2014.06.003. eCollection 2014. Leuk Res Rep. 2014. PMID: 25068104 Free PMC article.
-
Management of diffuse pontine gliomas in children: recent developments.Paediatr Drugs. 2013 Oct;15(5):351-62. doi: 10.1007/s40272-013-0033-5. Paediatr Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23719782 Review.
-
Kalanchoe tubiflora extract inhibits cell proliferation by affecting the mitotic apparatus.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012 Sep 10;12:149. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-12-149. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012. PMID: 22963191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams RR, Carmena M, Earnshaw WC. Chromosomal passengers and the (aurora) ABCs of mitosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:49–54. - PubMed
-
- Meraldi P, Honda R, Nigg EA. Aurora kinases link chromosome segregation and cell division to cancer susceptibility. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004;14:29–36. - PubMed
-
- Mendez R, Hake LE, Andresson T, Littlepage LE, Ruderman JV, Richter JD. Phosphorylation of CPE binding factor by Eg2 regulates translation of c-mos mRNA. Nature. 2000;404:302–7. - PubMed
-
- Giet R, Prigent C. Aurora/Ipl1p-related kinases, a new oncogenic family of mitotic serine-threonine kinases. J Cell Sci. 1999;112(Pt 21):3591–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

