Prolactin inhibits BCL6 expression in breast cancer through a Stat5a-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 20124477
- PMCID: PMC2822876
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2314
Prolactin inhibits BCL6 expression in breast cancer through a Stat5a-dependent mechanism
Abstract
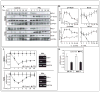
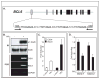
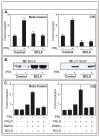
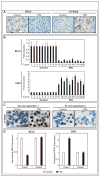
BCL6 is a transcriptional repressor that recognizes DNA target sequences similar to those recognized by signal transducer and activator of transcriptions 5 (Stat5). BCL6 disrupts differentiation of breast epithelia, is downregulated during lactation, and is upregulated in poorly differentiated breast cancer. In contrast, Stat5a mediates prolactin-induced differentiation of mammary epithelia, and loss of Stat5 signaling in human breast cancer is associated with undifferentiated histology and poor prognosis. Here, we identify the mammary cell growth factor prolactin as a potent suppressor of BCL6 protein expression in human breast cancer through a mechanism that requires Stat5a, but not prolactin-activated Stat5b, MEK-ERK, or PI3K-AKT pathways. Prolactin rapidly suppressed BCL6 mRNA in T47D, MCF7, ZR75.1, and SKBr3 breast cancer cell lines, followed by prolonged reduction of BCL6 protein levels within 3 hours. Prolactin suppression of BCL6 was enhanced by overexpression of Stat5a but not Stat5b, was mimicked by constitutively active Stat5a, but did not require the transactivation domain of Stat5a. Stat5 chromatin immunoprecipitation demonstrated physical interaction with a BCL6 gene regulatory region, and BCL6 transcript repression required histone deacetylase activity based on sensitivity to trichostatin A. Functionally, BCL6 overexpression disrupted prolactin induction of Stat5 reporter genes. Prolactin suppression of BCL6 was extended to xenotransplant tumors in nude mice in vivo and to freshly isolated human breast cancer explants ex vivo. Quantitative immunohistochemistry revealed elevated BCL6 in high-grade and metastatic breast cancer compared with ductal carcinoma in situ and nonmalignant breast, and cellular BCL6 protein levels correlated negatively with nuclear Stat5a (r = -0.52; P < 0.001) but not with Stat5b. Loss of prolactin-Stat5a signaling and concomitant upregulation of BCL6 may represent a regulatory switch facilitating undifferentiated histology and poor prognosis of breast cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)-5A and STAT5B differentially regulate human mammary carcinoma cell behavior.Endocrinology. 2010 Jan;151(1):43-55. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0651. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 19966185
-
Role of c-Myb during prolactin-induced signal transducer and activator of transcription 5a signaling in breast cancer cells.Endocrinology. 2009 Apr;150(4):1597-606. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-1079. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19036881 Free PMC article.
-
Prolactin suppresses a progestin-induced CK5-positive cell population in luminal breast cancer through inhibition of progestin-driven BCL6 expression.Oncogene. 2014 Apr 24;33(17):2215-24. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.172. Epub 2013 May 27. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23708665 Free PMC article.
-
Stat5a and Stat5b: fraternal twins of signal transduction and transcriptional activation.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1999 Jun;10(2):131-57. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(99)00011-8. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1999. PMID: 10743504 Review.
-
Interpretation of cytokine signaling through the transcription factors STAT5A and STAT5B.Genes Dev. 2008 Mar 15;22(6):711-21. doi: 10.1101/gad.1643908. Genes Dev. 2008. PMID: 18347089 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The feedback loop of LITAF and BCL6 is involved in regulating apoptosis in B cell non-Hodgkin's-lymphoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 22;7(47):77444-77456. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12680. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27764808 Free PMC article.
-
Notch3 restricts metastasis of breast cancers through regulation of the JAK/STAT5A signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2023 Dec 20;23(1):1257. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11746-w. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38124049 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of STAT3 and STAT5 signaling on gene regulation and chromatin remodeling in hematopoietic cancer.Leukemia. 2018 Aug;32(8):1713-1726. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0117-x. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Leukemia. 2018. PMID: 29728695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STAT5A-mediated SOCS2 expression regulates Jak2 and STAT3 activity following c-Src inhibition in head and neck squamous carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 1;18(1):127-39. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1889. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22090359 Free PMC article.
-
An N-terminal splice variant of human Stat5a that interacts with different transcription factors is the dominant form expressed in invasive ductal carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2014 Apr 28;346(1):148-57. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.12.030. Epub 2013 Dec 30. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 24384092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu X, Robinson GW, Wagner KU, Garrett L, Wynshaw-Boris A, Hennighausen L. Stat5a is mandatory for adult mammary gland development and lactogenesis. Genes Dev. 1997;11:179–86. - PubMed
-
- Hennighausen L, Robinson GW, Wagner KU, Liu W. Prolactin signaling in mammary gland development. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:7567–9. - PubMed
-
- Grimley PM, Dong F, Rui H. Stat5a and Stat5b: fraternal twins of signal transduction and transcriptional activation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1999;10:131–57. - PubMed
-
- Neilson LM, Zhu J, Xie J, et al. Coactivation of janus tyrosine kinase (Jak)1 positively modulates prolactin-Jak2 signaling in breast cancer: recruitment of ERK and signal transducer and activator of transcription (Stat)3 and enhancement of Akt and Stat5a/b pathways. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21:2218–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

