Noncoding RNA gas5 is a growth arrest- and starvation-associated repressor of the glucocorticoid receptor
- PMID: 20124551
- PMCID: PMC2819218
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.2000568
Noncoding RNA gas5 is a growth arrest- and starvation-associated repressor of the glucocorticoid receptor
Abstract
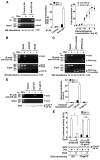
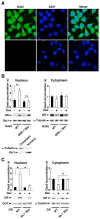
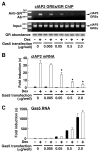
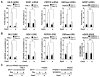
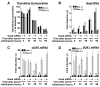
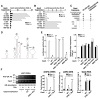
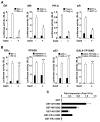
The availability of nutrients influences cellular growth and survival by affecting gene transcription. Glucocorticoids also influence gene transcription and have diverse activities on cell growth, energy expenditure, and survival. We found that the growth arrest-specific 5 (Gas5) noncoding RNA, which is abundant in cells whose growth has been arrested because of lack of nutrients or growth factors, sensitized cells to apoptosis by suppressing glucocorticoid-mediated induction of several responsive genes, including the one encoding cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 2. Gas5 bound to the DNA-binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) by acting as a decoy glucocorticoid response element (GRE), thus competing with DNA GREs for binding to the GR. We conclude that Gas5 is a "riborepressor" of the GR, influencing cell survival and metabolic activities during starvation by modulating the transcriptional activity of the GR.
Figures

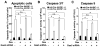

References
-
- Lopez-Maury L, Marguerat S, Bahler J. Tuning gene expression to changing environments: from rapid responses to evolutionary adaptation. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:583–593. - PubMed
-
- Sellick CA, Reece RJ. Eukaryotic transcription factors as direct nutrient sensors. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30:405–412. - PubMed
-
- Kino T, Chrousos GP. Glucocorticoid Effect on Gene Expression. In: Steckler T, Kalin NH, Reul JMHM, editors. Handbook on Stress and the Brain Part 1. Elsevier BV; Amsterdam: 2004. pp. 295–312.
-
- Chrousos GP. Glucocorticoid therapy. In: Felig P, Frohman LA, editors. Endocrinology & Metablism. McGraw-Hill; New York: 2001. pp. 609–632.
-
- Chrousos GP, Kino T. Intracellular glucocorticoid signaling: a formerly simple system turns stochastic. Sci STKE 2005. 2005:pe48. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

