Structure of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens alpha-amylase at high resolution: implications for thermal stability
- PMID: 20124706
- PMCID: PMC2815676
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309109051938
Structure of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens alpha-amylase at high resolution: implications for thermal stability
Abstract
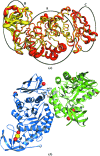
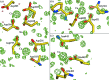
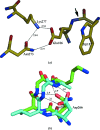
The crystal structure of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens alpha-amylase (BAA) at 1.4 A resolution revealed ambiguities in the thermal adaptation of homologous proteins in this family. The final model of BAA is composed of two molecules in a back-to-back orientation, which is likely to be a consequence of crystal packing. Despite a high degree of identity, comparison of the structure of BAA with those of other liquefying-type alpha-amylases indicated moderate discrepancies at the secondary-structural level. Moreover, a domain-displacement survey using anisotropic B-factor and domain-motion analyses implied a significant contribution of domain B to the total flexibility of BAA, while visual inspection of the structure superimposed with that of B. licheniformis alpha-amylase (BLA) indicated higher flexibility of the latter in the central domain A. Therefore, it is suggested that domain B may play an important role in liquefying alpha-amylases, as its rigidity offers a substantial improvement in thermostability in BLA compared with BAA.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of calcium-depleted Bacillus licheniformis alpha-amylase at 2.2 A resolution.J Mol Biol. 1995 Mar 3;246(4):545-59. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0106. J Mol Biol. 1995. PMID: 7877175
-
Crystal structure of thermostable alpha-amylase from Bacillus licheniformis refined at 1.7 A resolution.Mol Cells. 1997 Apr 30;7(2):251-8. Mol Cells. 1997. PMID: 9163741
-
Investigation on the effects of three X-->histidine replacements on thermostability of alpha-amylase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 May;22(5):592-9. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1109.09009. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22561851
-
Probing structural determinants specifying high thermostability in Bacillus licheniformis alpha-amylase.J Mol Biol. 2000 Aug 25;301(4):1041-57. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4025. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10966804
-
Structural and dynamical features contributing to thermostability in alpha-amylases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005 Sep;62(17):1925-37. doi: 10.1007/s00018-005-5079-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 15990960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Close relationship of a novel Flavobacteriaceae α-amylase with archaeal α-amylases and good potentials for industrial applications.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2014 Jan 31;7(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1754-6834-7-18. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2014. PMID: 24485248 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and cooperative stabilization of a two-metal (Ca, Zn) center in α-amylase derived from Flavobacteriaceae species.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 20;7(1):17933. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18085-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29263337 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence and structural investigation of a novel psychrophilic α-amylase from Glaciozyma antarctica PI12 for cold-adaptation analysis.J Mol Model. 2013 Aug;19(8):3369-83. doi: 10.1007/s00894-013-1861-5. Epub 2013 May 18. J Mol Model. 2013. PMID: 23686283
-
Structural and functional adaptation in extremophilic microbial α-amylases.Biophys Rev. 2022 Jan 24;14(2):499-515. doi: 10.1007/s12551-022-00931-z. eCollection 2022 Apr. Biophys Rev. 2022. PMID: 35528036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular cloning, expression, and biochemical characterization of a novel cold-active α-amylase from Bacillus sp. dsh19-1.Extremophiles. 2018 Sep;22(5):739-749. doi: 10.1007/s00792-018-1034-7. Epub 2018 Jun 23. Extremophiles. 2018. PMID: 29936543
References
-
- Aghajari, N., Feller, G., Gerday, C. & Haser, R. (1998). Structure, 6, 1503–1516. - PubMed
-
- Brünger, A. T. (1992). Nature (London), 355, 472–475. - PubMed
-
- Brünger, A. T., Adams, P. D., Clore, G. M., DeLano, W. L., Gros, P., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W., Jiang, J.-S., Kuszewski, J., Nilges, M., Pannu, N. S., Read, R. J., Rice, L. M., Simonson, T. & Warren, G. L. (1998). Acta Cryst. D54, 905–921. - PubMed
-
- Brzozowski, A. M., Lawson, D. M., Turkenburg, J. P., Bisgaard-Frantzen, H., Svendsen, A., Borchert, T. V., Dauter, Z., Wilson, K. S. & Davies, G. J. (2000). Biochemistry, 33, 9099–9107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

