Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analyses of the homodimeric glycine decarboxylase (P-protein) from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
- PMID: 20124719
- PMCID: PMC2815689
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309109052828
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analyses of the homodimeric glycine decarboxylase (P-protein) from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
Abstract
Glycine decarboxylase, or P-protein, is a major enzyme that is involved in the C(1) metabolism of all organisms and in the photorespiratory pathway of plants and cyanobacteria. The protein from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 is a homodimer with a mass of 215 kDa. Recombinant glycine decarboxylase was expressed in Escherichia coli and purified by metal-affinity, ion-exchange and gel-filtration chromatography. Crystals of P-protein that diffracted to a resolution of 2.1 A were obtained using the hanging-drop vapour-diffusion method at 291 K. X-ray diffraction data were collected from cryocooled crystals using synchrotron radiation. The crystals belonged to space group P2(1)2(1)2(1), with unit-cell parameters a = 96.30, b = 135.81, c = 179.08 A.
Figures

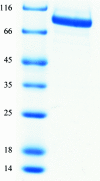

References
-
- Douce, R., Bourguignon, J., Neuburger, M. & Rebeille, F. (2001). Trends Plant Sci.6, 167–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

