Preoperative weight reduction using the intragastric balloon
- PMID: 20124772
- PMCID: PMC6444689
- DOI: 10.1159/000198243
Preoperative weight reduction using the intragastric balloon
Abstract
Background: Gastric balloon therapy (GBT) is a temporary, nonsurgical treatment for obesity. This retrospective study evaluates safety and efficacy of GBT in obese patients.
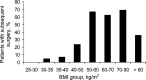
Methods: The BioEnterics. Intragastric Balloon (BIB) was endoscopically implanted into each patient's stomach and inflated with saline (450-750 ml). Extraction was planned after 6 months. Data from 190 patients receiving GBT were evaluated. Mean weight was 168.4 +/- 58.9 kg (range 76.5-310.0) and mean BMI was 55.6 +/- 17.5 kg/m2 (range 27.0-95.7).
Results: Mean weight loss at the time of balloon removal was 21.2 +/- 14.0 kg (range 0-80.0). The mean BMI loss and EBL(Excess BMI Loss) were 7.2 +/- 4.9 kg/m2 (range 0-28.9) and 30.1 +/- 26.4% (0-184.4), respectively. The most substantial weight and BMI loss was observed in the most massively obese patients. Minor complications at implantation were encountered in 2 cases (1.1%) due to leakage of the balloon, and in 3 cases at explantation (1.6%). No mortality or major complications such as gastric perforation or ulcers occurred. Of the 190 patients, 76 received subsequent surgery (40.0%). Of those, 7 patients had a BMI < 50 kg/m2 while all other patients where super-obese (BMI > 50 kg/m2). 58 patients (30.5%) with a BMI > 60 kg/m2 which had an extraordinary high operation risk were able to receive subsequent surgical treatment because of a substantial weight loss and/or reduced comorbidity.
Conclusion: GBT appears to be a safe, tolerable, and potentially effective procedure for the initial treatment of morbid obesity.
Figures

References
-
- Genco A, Bruni T, Doldi SB, Forestieri P, Marino M, Busetto L, Giardiello C, Angrisani L, Pecchioli L, Stornelli P, Puglisi F, Alkilani M, Nigri A, Di Lorenzo N, Furbetta F, Cascardo A, Cipriano M, Lorenzo M, Basso N. BioEnterics Intragastric Balloon: The Italian experience with 2,515 patients. Obes Surg. 2005;15:1161–1164. - PubMed
-
- Fernandes M, Atallah AN, Soares BG, Humberto S, Guimarães S, Matos D, Monteiro L, Richter B. Intragastric balloon for obesity. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;1:CD004931. www.cochrane.org/reviews/en/ab004931.html. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martinez-Brocca MA, Belda O, Parejo J, Jimenez L, del Valle A, Pereira JL, Garcia-Pesquera F, Astorga R, Leal-Cerro A, Garcia-Luna PP. Intragastric balloon-induced satiety is not mediated by modification in fasting or postprandial plasma ghrelin levels in morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 2007;17:649–657. - PubMed
-
- Pasulka PS, Bistrian BR, Benotti PN, Blackburn GL. The risks of surgery in obese patients. Ann Intern Med. 1986;104:540–6. - PubMed
-
- Imaz I, Martínez-Cervell C, García-Alvarez EE, Sendra-Gutiérrez JM, González-Enríquez J, Safety and effectiveness of the intragastric balloon for obesity A meta-analysis. Obes Surg. 2008;18:841–846. - PubMed

