Role of coagulation factors in cerebral venous sinus and cerebral microvascular thrombosis
- PMID: 20124931
- PMCID: PMC3089420
- DOI: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000365745.49583.FD
Role of coagulation factors in cerebral venous sinus and cerebral microvascular thrombosis
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to define the relative contributions of three major pro- and anti-coagulation pathways (heparin-antithrombin, protein C, and tissue factor (TF)) in the thrombogenic responses that occur in large and small vessels of the brain.
Methods: Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis was induced by topical application of FeCl3 on the superior sagittal sinus, while photoactivation of fluorescein was used to induce thrombus formation in cerebral microvessels. Heparin, activated protein C (APC), and antibodies to either APC or TF were used to assess thrombogenesis in wild-type mice. Mutant mice that overexpress the endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR-tg) or with TF deficiency in Tie2-expressing endothelial cells (LTFE) were also used.
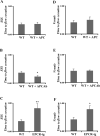
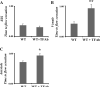
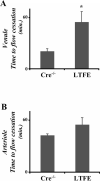
Results: Thrombus formation in the superior sagittal sinus of wild-type mice was attenuated by heparin and in EPCR-tg mice, while treatment with the APC antibodies enhanced thrombogenesis. Arteriolar thrombosis was largely unresponsive to the interventions studied. However, in cerebral venules, thrombosis was inhibited by heparin and in EPCR-tg mice. TF antibody treatment also inhibited venular thrombosis, with a similar attenuation noted in LTFE mice.
Conclusion: Thrombin promotes while the APC pathway blunts thrombus formation in an experimental model of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. TF involvement is more evident in cerebral microvascular thrombogenesis, with endothelial cell-associated TF mediating this response in venules, but not arterioles.
Figures


References
-
- Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M, Davis SM. Stroke. Lancet. 2008 May 10;371(9624):1612–1623. - PubMed
-
- Pinel C, Wice SM, Hiebert LM. Orally administered heparins prevent arterial thrombosis in a rat model. Thromb Haemost. 2004 May;91(5):919–926. - PubMed
-
- Rumbaut RE, Slaff DW, Burns AR. Microvascular thrombosis models in venules and arterioles in vivo. Microcirculation. 2005 Apr-May;12(3):259–274. - PubMed
-
- Maxwell KA, Dyck RH. Induction of reproducible focal ischemic lesions in neonatal mice by photothrombosis. Dev Neurosci. 2005 Mar-Aug;27(2-4):121–126. - PubMed
-
- Kurz KD, Main BW, Sandusky GE. Rat model of arterial thrombosis induced by ferric chloride. Thromb Res. 1990 Nov 15;60(4):269–280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

