Bone marrow stromal cells enhance inter- and intracortical axonal connections after ischemic stroke in adult rats
- PMID: 20125183
- PMCID: PMC2896436
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.8
Bone marrow stromal cells enhance inter- and intracortical axonal connections after ischemic stroke in adult rats
Abstract
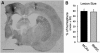
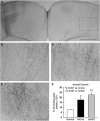
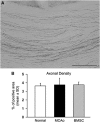
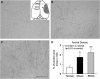
We investigated axonal plasticity in the bilateral motor cortices in rats after unilateral stroke and bone marrow stromal cell (BMSC) treatment. Rats were subjected to permanent right middle cerebral artery occlusion followed by intravenous administration of phosphate-buffered saline or BMSCs 1 day later. Adhesive-removal test and modified neurologic severity score were performed weekly to monitor limb functional deficit and recovery. Anterograde tracing with biotinylated dextran amine injected into the right motor cortex was used to assess axonal sprouting in the contralateral motor cortex and ipsilateral rostral forelimb area. Animals were killed 28 days after stroke. Progressive functional recovery was significantly enhanced by BMSCs. Compared with normal animals, axonal density in both contralateral motor cortex and ipsilateral rostral forelimb area significantly increased after stroke. Bone marrow stromal cells markedly enhanced such interhemispheric and intracortical connections. However, labeled transcallosal axons in the corpus callosum were not altered with either stroke or treatment. Both interhemispheric and intracortical axonal sprouting were significantly and highly correlated with behavioral outcome after stroke. This study suggests that, after stroke, cortical neurons surviving in the peri-infarct motor cortex undergo axonal sprouting to restore connections between different cerebral areas. Bone marrow stromal cells enhance axonal plasticity, which may underlie neurologic functional improvement.
Figures
References
-
- Carmichael ST. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of neural repair after stroke: making waves. Ann Neurol. 2006;59:735–742. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Zhang ZG, Li Y, Wang L, Xu YX, Gautam SC, Lu M, Zhu Z, Chopp M. Intravenous administration of human bone marrow stromal cells induces angiogenesis in the ischemic boundary zone after stroke in rats. Circ Res. 2003;92:692–699. - PubMed
-
- Conner JM, Chiba AA, Tuszynski MH. The basal forebrain cholinergic system is essential for cortical plasticity and functional recovery following brain injury. Neuron. 2005;46:173–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

