Endogenous Nmnat2 is an essential survival factor for maintenance of healthy axons
- PMID: 20126265
- PMCID: PMC2811159
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000300
Endogenous Nmnat2 is an essential survival factor for maintenance of healthy axons
Abstract
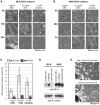
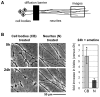
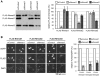
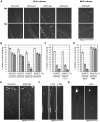
The molecular triggers for axon degeneration remain unknown. We identify endogenous Nmnat2 as a labile axon survival factor whose constant replenishment by anterograde axonal transport is a limiting factor for axon survival. Specific depletion of Nmnat2 is sufficient to induce Wallerian-like degeneration of uninjured axons which endogenous Nmnat1 and Nmnat3 cannot prevent. Nmnat2 is by far the most labile Nmnat isoform and is depleted in distal stumps of injured neurites before Wallerian degeneration begins. Nmnat2 turnover is equally rapid in injured Wld(S) neurites, despite delayed neurite degeneration, showing it is not a consequence of degeneration and also that Wld(S) does not stabilize Nmnat2. Depletion of Nmnat2 below a threshold level is necessary for axon degeneration since exogenous Nmnat2 can protect injured neurites when expressed at high enough levels to overcome its short half-life. Furthermore, proteasome inhibition slows both Nmnat2 turnover and neurite degeneration. We conclude that endogenous Nmnat2 prevents spontaneous degeneration of healthy axons and propose that, when present, the more long-lived, functionally related Wld(S) protein substitutes for Nmnat2 loss after axon injury. Endogenous Nmnat2 represents an exciting new therapeutic target for axonal disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors and host institution have a patent pending related to this work.
Figures
References
-
- Araki T, Sasaki Y, Milbrandt J. Increased nuclear NAD biosynthesis and SIRT1 activation prevent axonal degeneration. Science. 2004;305:1010–1013. - PubMed
-
- Conforti L, Fang G, Beirowski B, Wang M. S, Sorci L, et al. NAD(+) and axon degeneration revisited: Nmnat1 cannot substitute for WldS to delay Wallerian degeneration. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:116–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

