Westward ho! Pioneering mouse models for x-linked infantile spasms syndrome
- PMID: 20126336
- PMCID: PMC2812720
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1535-7511.2009.01343.x
Westward ho! Pioneering mouse models for x-linked infantile spasms syndrome
Figures
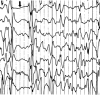
Comment on
-
Targeted loss of Arx results in a developmental epilepsy mouse model and recapitulates the human phenotype in heterozygous females.Brain. 2009 Jun;132(Pt 6):1563-76. doi: 10.1093/brain/awp107. Epub 2009 May 12. Brain. 2009. PMID: 19439424 Free PMC article.
-
A triplet repeat expansion genetic mouse model of infantile spasms syndrome, Arx(GCG)10+7, with interneuronopathy, spasms in infancy, persistent seizures, and adult cognitive and behavioral impairment.J Neurosci. 2009 Jul 8;29(27):8752-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0915-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19587282 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Infantile spasms in down syndrome: Rescue by knockdown of the GIRK2 channel.Ann Neurol. 2016 Oct;80(4):511-21. doi: 10.1002/ana.24749. Epub 2016 Aug 13. Ann Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27462820
-
Infantile spasms and Down syndrome: a new animal model.Pediatr Res. 2009 May;65(5):499-503. doi: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e31819d9076. Pediatr Res. 2009. PMID: 19190545
-
Confirmation of linkage in X-linked infantile spasms (West syndrome) and refinement of the disease locus to Xp21.3-Xp22.1.Clin Genet. 1999 Mar;55(3):173-81. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0004.1999.550305.x. Clin Genet. 1999. PMID: 10334471
-
Pathogenesis and new candidate treatments for infantile spasms and early life epileptic encephalopathies: A view from preclinical studies.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Jul;79:135-49. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.04.015. Epub 2015 May 9. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 25968935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infantile spasms and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.J Child Neurol. 2002 Feb;17 Suppl 2:2S9-2S22. doi: 10.1177/08830738020170021201. J Child Neurol. 2002. PMID: 11952036 Review.
References
-
- Wong M, Trevathan E. Infantile spasms. Pediatr Neurol. 2001;24:89–98. - PubMed
-
- Freeman JM. In: Brain Development and Epilepsy. Moshe SL, Schwartzkroin PA, Noebels JL, Swann JW, editors. New York: Oxford University Press; 1995. pp. 9–33. Vol. 1.
-
- Saitsu H, Kato M, Mizuguchi T, Hamada K, Osaka H, Tohyama J, Uruno K, Kumada S, Nishiyama K, Nishimura A, Okada I, Yoshimura Y, Hirai S, Kumada T, Hayasaka K, Fukuda A, Ogata K, Matsumoto N. De novo mutations in the gene encoding STXBP1 (MUNC18-1) cause early infantile epileptic encephalopathy. Nat Genet. 2008;40:782–788. - PubMed
-
- Toonen RF, Verhage M. Munc18-1 in secretion: Lonely Munc joins SNARE team and takes control. Trends Neurosci. 2007;30:564–572. - PubMed
-
- Marshall CR, Young EJ, Pani AM, Freckmann ML, Lacassie Y, Howald C, Fitzgerald KK, Peippo M, Morris CA, Shane K, Priolo M, Morimoto M, Kondo I, Manguoglu E, Berker-Karauzum S, Edery P, Hobart HH, Mervis CB, Zuffardi O, Reymond A, Kaplan P, Tassabehji M, Gregg RG, Scherer SW, Osborne LR. Infantile spasms is associated with deletion of the MAGI2 gene on chromosome 7q11.23-q21.11. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;83:106–111. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

