Polymerase chain reaction-based clonality analysis of cutaneous B-cell lymphoproliferative processes
- PMID: 20126346
- PMCID: PMC2815283
- DOI: 10.1590/S1807-59322010000100009
Polymerase chain reaction-based clonality analysis of cutaneous B-cell lymphoproliferative processes
Abstract
Introduction: The differential diagnosis of B-cell lymphoproliferative processes remains a challenge for pathologists, dermatologists and oncologists, despite advances in histology, immunohistochemistry and molecular biology.
Objective: Evaluate aid and limitations of clonality analysis in the diagnosis of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas and B-cell pseudolymphomas.
Methods: This study included 29 cases of B-cell lymphoproliferative processes classified as primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas (13), B-cell pseudolymphomas (6) and inconclusive cases (10) using histology and immunohistochemistry. The clonality analysis was performed by polymerase chain reaction analysis of immunoglobulin light chain and heavy chain rearrangements.
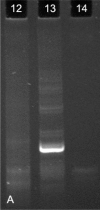
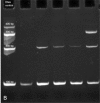
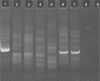
Results: DNA quality was shown to be generally poor; eight samples were inadequate for polymerase chain reaction analysis. The results showed monoclonality in eight of the primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas and polyclonality in four of the B-cell pseudolymphomas. In addition, monoclonality was shown in two of the inconclusive cases by histology and immunohistochemistry, demonstrating the utility of polymerase chain reaction as an ancillary diagnostic tool for primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas.
Discussion: The low quality DNA extracted from these cases demanded the use of an IgH protocol that yielded small fragments and IgK. Both methods used together improved detection.
Conclusion: Use of the two protocols, immunoglobulin heavy chain FR3-trad and immunoglobulin light chain-Kappa Biomed protocols for clonality analysis improved diagnostic accuracy.
Keywords: B-cell; Clonality; Cutaneous lymphoma; Gene rearrangement; Lymphoproliferative processes; Polymerase chain reaction.
Figures
References
-
- Burg G, Kerl H, Przybilla B, Braun-Falco O. Some statistical data, diagnosis, and staging of cutaneous B-cell lymphomas. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1984;10:256–62. - PubMed
-
- Cerroni L, Kerl H. Diagnostic immunohistology: cutaneous lymphomas and pseudolymphomas. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1999;18:64–70. - PubMed
-
- Holm N, Flaig MJ, Yazdi AS, Sander CA. The value of molecular analysis by PCR in the diagnosis of cutaneous lymphocytic infiltrates. J Cutan Pathol. 2002;29:447–52. - PubMed
-
- Rijlaarsdam U, Bakels V, van Oostveen JW, Gordijn RJ, Geerts ML, Meijer CJ, et al. Demonstration of clonal immunoglobulin gene rearrangements in cutaneous B-cell lymphomas and pseudo-B-cell lymphomas: differential diagnostic and pathogenetic aspects. J Invest Dermatol. 1992;99:749–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

