The effect of eurycoma longifolia Jack on spermatogenesis in estrogen-treated rats
- PMID: 20126351
- PMCID: PMC2815289
- DOI: 10.1590/S1807-59322010000100014
The effect of eurycoma longifolia Jack on spermatogenesis in estrogen-treated rats
Abstract
Introduction: There is little data concerning the ability of Eurycoma longifolia Jack (EL) to reverse the inhibitory effects of estrogen on testosterone production and spermatogenesis. The aim of the present study was to determine the effect of EL on testicular histology and sperm count in estrogen-treated male rats.
Methods: Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 200-250 g were divided into four groups of six rats each. Group A (control) was given solvent in the same manner as the treated groups were given EL. Group B was treated with EL (8 mg/kg body weight) orally. Group C was treated with estradiol (E(2)) (intramuscular dose of 500 microg/kg body weight), and group D received a combined treatment of oral EL and intramuscular E(2). After fourteen consecutive days of treatment, rats from all groups were sacrificed and subjected to spermatogenic and epididymal sperm cell counts.
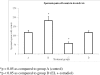
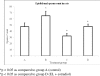
Results: The spermatogenic cell count in the E(2)-treated group was significantly decreased as compared to the control (p < 0.05) and EL+E(2)-treated groups (p < 0.05). A similar finding was found for the epididymal sperm count; the E(2)-treated group had a significant decrease in the count compared to the control (p < 0.05) and EL+E(2)-treated groups (p < 0.05). Rats that were treated with EL alone exhibited significantly higher sperm counts and sperm motility when compared to the control group (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: EL extract acts as a potential agent for reversing the effects of estrogen by increasing spermatogenesis and sperm counts in rats after fourteen consecutive days of treatment.
Keywords: Anatomy; Estrogen; Eurycoma longifolia Jack; Histology; Spermatogenesis; Testis.
Figures


References
-
- Tee TT, Cheah YH, Hawariah LP. F16, a fraction from Eurycoma longifolia jack extract, induces apoptosis via a caspase-9-independent manner in MCF-7 cells. Anticancer Res. 2007;27:3425–30. - PubMed
-
- Farouk AE, Benafri A. Antibacterial activity of Eurycoma longifolia Jack. A Malaysian medicinal plant. Saudi Med J. 2007;28:1422–4. - PubMed
-
- Kuo PC, Damu AG, Lee KH, Wu TS. Cytotoxic and antimalarial constituents from the roots of Eurycoma longifolia. Bioorg Med Chem. 2004;12:537–44. - PubMed
-
- Kuo PC, Shi LS, Damu AG, et al. Cytotoxic and antimalarial beta-carboline alkaloids from the roots of Eurycoma longifolia. J Nat Prod. 2003;66:1324–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

