Regulatory T cells and human myeloid dendritic cells promote tolerance via programmed death ligand-1
- PMID: 20126379
- PMCID: PMC2814822
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000302
Regulatory T cells and human myeloid dendritic cells promote tolerance via programmed death ligand-1
Abstract
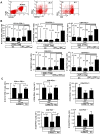
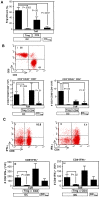
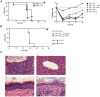
Immunotherapy using regulatory T cells (Treg) has been proposed, yet cellular and molecular mechanisms of human Tregs remain incompletely characterized. Here, we demonstrate that human Tregs promote the generation of myeloid dendritic cells (DC) with reduced capacity to stimulate effector T cell responses. In a model of xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), allogeneic human DC conditioned with Tregs suppressed human T cell activation and completely abrogated posttransplant lethality. Tregs induced programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression on Treg-conditioned DC; subsequently, Treg-conditioned DC induced PD-L1 expression in vivo on effector T cells. PD-L1 blockade reversed Treg-conditioned DC function in vitro and in vivo, thereby demonstrating that human Tregs can promote immune suppression via DC modulation through PD-L1 up-regulation. This identification of a human Treg downstream cellular effector (DC) and molecular mechanism (PD-L1) will facilitate the rational design of clinical trials to modulate alloreactivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Sakaguchi S, Ono M, Setoguchi R, Yagi H, Hori S, et al. Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ natural regulatory T cells in dominant self-tolerance and autoimmune disease. Immunol Rev. 2006;212:8–27. - PubMed
-
- Brunkow M. E, Jeffery E. W, Hjerrild K. A, Paeper B, Clark L. B, et al. Disruption of a new forkhead/winged-helix protein, scurfin, results in the fatal lymphoproliferative disorder of the scurfy mouse. Nat Genet. 2001;27:68–73. - PubMed
-
- Bennett C. L, Christie J, Ramsdell F, Brunkow M. E, Ferguson P. J, et al. The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat Genet. 2001;27:20–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

