Differential expression of hERG1 channel isoforms reproduces properties of native I(Kr) and modulates cardiac action potential characteristics
- PMID: 20126398
- PMCID: PMC2814852
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009021
Differential expression of hERG1 channel isoforms reproduces properties of native I(Kr) and modulates cardiac action potential characteristics
Abstract
Background: The repolarizing cardiac rapid delayed rectifier current, I(Kr), is composed of ERG1 channels. It has been suggested that two isoforms of the ERG1 protein, ERG1a and ERG1b, both contribute to I(Kr). Marked heterogeneity in the kinetic properties of native I(Kr) has been described. We hypothesized that the heterogeneity of native I(Kr) can be reproduced by differential expression of ERG1a and ERG1b isoforms. Furthermore, the functional consequences of differential expression of ERG1 isoforms were explored as a potential mechanism underlying native heterogeneity of action potential duration (APD) and restitution.
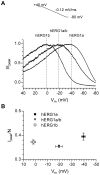
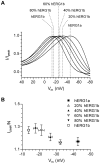
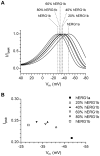
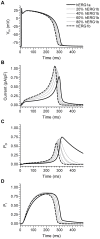
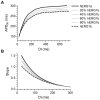
Methodology/principal findings: The results show that the heterogeneity of native I(Kr) can be reproduced in heterologous expression systems by differential expression of ERG1a and ERG1b isoforms. Characterization of the macroscopic kinetics of ERG1 currents demonstrated that these were dependent on the relative abundance of ERG1a and ERG1b. Furthermore, we used a computational model of the ventricular cardiomyocyte to show that both APD and the slope of the restitution curve may be modulated by varying the relative abundance of ERG1a and ERG1b. As the relative abundance of ERG1b was increased, APD was gradually shortened and the slope of the restitution curve was decreased.
Conclusions/significance: Our results show that differential expression of ERG1 isoforms may explain regional heterogeneity of I(Kr) kinetics. The data demonstrate that subunit dependent changes in channel kinetics are important for the functional properties of ERG1 currents and hence I(Kr). Importantly, our results suggest that regional differences in the relative abundance of ERG1 isoforms may represent a potential mechanism underlying the heterogeneity of both APD and APD restitution observed in mammalian hearts.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
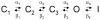
References
-
- Sanguinetti MC, Jiang C, Curran ME, Keating MT. A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel. Cell. 1995;81:299–307. - PubMed
-
- Trudeau MC, Warmke JW, Ganetzky B, Robertson GA. HERG, a human inward rectifier in the voltage-gated potassium channel family. Science. 1995;269:92–95. - PubMed
-
- Curran ME, Splawski I, Timothy KW, Vincent GM, Green ED, et al. A molecular basis for cardiac arrhythmia: HERG mutations cause long QT syndrome. Cell. 1995;80:795–803. - PubMed
-
- Brugada R, Hong K, Dumaine R, Cordeiro J, Gaita F, et al. Sudden death associated with short-QT syndrome linked to mutations in HERG. Circulation. 2004;109:30–35. - PubMed
-
- Jones EM, Roti Roti EC, Wang J, Delfosse SA, Robertson GA. Cardiac IKr channels minimally comprise hERG 1a and 1b subunits. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:44690–44694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

