A mutant of hepatitis B virus X protein (HBxDelta127) promotes cell growth through a positive feedback loop involving 5-lipoxygenase and fatty acid synthase
- PMID: 20126469
- PMCID: PMC2814349
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.91298
A mutant of hepatitis B virus X protein (HBxDelta127) promotes cell growth through a positive feedback loop involving 5-lipoxygenase and fatty acid synthase
Abstract
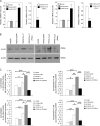
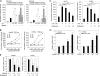
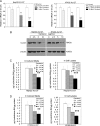
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignant tumors worldwide. Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) contributes to the development of HCC, whereas HBx with COOH-terminal deletion is a frequent event in the HCC tissues. Previously, we identified a natural mutant of HBx-truncated 27 amino acids at the COOH-terminal (termed HBxDelta127), which strongly enhanced cell growth. In the present study, we focused on investigating the mechanism. Accordingly, fatty acid synthase (FAS) plays a crucial role in cancer cell survival and proliferation; thus, we examined the signaling pathways involving FAS. Our data showed that HBxDelta127 strongly increased the transcriptional activities of FAS in human hepatoma HepG2 and H7402 cells. Moreover, we found that 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) was responsible for the up-regulation of FAS by using MK886 (an inhibitor of 5-LOX) and 5-LOX small interfering RNA. We observed that HBxDelta127 could upregulate 5-LOX through phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1/2 and thus resulted in the increase of released leukotriene B4 (LTB4, a metabolite of 5-LOX) by ELISA. The additional LTB4 could upregulate the expression of FAS in the cells as well. Interestingly, we found that FAS was able to upregulate the expression of 5-LOX in a feedback manner by using cerulenin (an inhibitor of FAS). Collectively, HBxDelta127 promotes cell growth through a positive feedback loop involving 5-LOX and FAS, in which released LTB4 is involved in the up-regulation of FAS. Thus, our finding provides a new insight into the mechanism involving the promotion of cell growth mediated by HBxDelta127.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
