Synthetic Musk Fragrances in a Conventional Drinking Water Treatment Plant with Lime Softening
- PMID: 20126513
- PMCID: PMC2790179
- DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0000085
Synthetic Musk Fragrances in a Conventional Drinking Water Treatment Plant with Lime Softening
Abstract
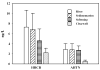
Synthetic musk fragrances are common personal care product additives and wastewater contaminants that are routinely detected in the environment. This study examines the presence eight synthetic musk fragrances (AHTN, HHCB, ATII, ADBI, AHMI, musk xylene, and musk ketone) in source water and the removal of these compounds as they flow through a Midwestern conventional drinking water plant with lime softening. The compounds were measured in water, waste sludge, and air throughout the plant. HHCB and AHTN were detected in 100% of the samples and at the highest concentrations. A mass balance on HHCB and AHTN was performed under warm and cold weather conditions. The total removal efficiency for HHCB and AHTN, which averaged between 67% to 89%, is dominated by adsorption to water softener sludge and its consequent removal by sludge wasting and media filtration. Volatilization, chlorine disinfection, and the disposal of backwash water play a minor role in the removal of both compounds. As a result of inefficient overall removal, HHCB and AHTN are a constant presence at low levels in finished drinking water.
Figures

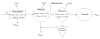
Similar articles
-
Synthetic musk fragrances in Lake Michigan.Environ Sci Technol. 2004 Jan 15;38(2):367-72. doi: 10.1021/es034769y. Environ Sci Technol. 2004. PMID: 14750709
-
Polycyclic musk fragrances in the aquatic environment.Toxicol Lett. 1999 Dec 20;111(1-2):37-56. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4274(99)00191-5. Toxicol Lett. 1999. PMID: 10630702 Review.
-
Synthetic musk fragrances in human milk from the United States.Environ Sci Technol. 2007 Jun 1;41(11):3815-20. doi: 10.1021/es063088a. Environ Sci Technol. 2007. PMID: 17612154
-
Synthetic musk fragrances in environmental Standard Reference Materials.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007 Apr;387(7):2381-8. doi: 10.1007/s00216-006-0671-3. Epub 2006 Aug 12. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007. PMID: 16906386
-
Analysis of musk fragrances in environmental samples.J Chromatogr A. 2009 Jan 16;1216(3):470-80. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2008.08.093. Epub 2008 Sep 2. J Chromatogr A. 2009. PMID: 18786673 Review.
Cited by
-
Could the musk compound tonalide affect physiological functions and act as an endocrine disruptor in rainbow trout?Physiol Res. 2020 Dec 31;69(Suppl 4):S595-S606. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934608. Physiol Res. 2020. PMID: 33656906 Free PMC article.
-
Designing field-based investigations of organic micropollutant fate in rivers.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Oct;26(28):28633-28649. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06058-1. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31385254
-
Synthesis of mixed musks via Eschenmoser-Tanabe fragmentation, enyne metathesis and Diels-Alder reaction as key steps.RSC Adv. 2022 May 11;12(22):14278-14281. doi: 10.1039/d2ra01458k. eCollection 2022 May 5. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35558836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reiner JL, Kannan K. A survey of polycyclic musks in selected household commodities from the United States. Chemosphere. 2006;62:867–873. - PubMed
-
- Yamagishi T, Miyazaki T, Horii S, Kaneko S. Identification of musk xylene and musk ketone in freshwater fish collected from the Tama River, (Tokyo) Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1981;26:656–662. - PubMed
-
- Peck AM, Hornbuckle KC. Synthetic musk fragrances in Lake Michigan. Environ Sci Technol. 2004;38:367–372. - PubMed
-
- Rimkus GG. Polycyclic musk fragrances in the aquatic environment. Toxicology Letters. 1999;111:37–56. - PubMed
-
- Kolpin DW, Skopec M, Meyer MT, Furlong ET, Zaugg SD. Urban contribution of pharmaceuticals and other organic wastewater contaminants to streams during differing flow conditions. Sci Tot Environ. 2004;328:119–130. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
