Effectiveness of common household cleaning agents in reducing the viability of human influenza A/H1N1
- PMID: 20126543
- PMCID: PMC2813869
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008987
Effectiveness of common household cleaning agents in reducing the viability of human influenza A/H1N1
Abstract
Background: In the event of an influenza pandemic, the majority of people infected will be nursed at home. It is therefore important to determine simple methods for limiting the spread of the virus within the home. The purpose of this work was to test a representative range of common household cleaning agents for their effectiveness at killing or reducing the viability of influenza A virus.
Methodology/principal findings: Plaque assays provided a robust and reproducible method for determining virus viability after disinfection, while a National Standard influenza virus RT-PCR assay (VSOP 25, www.hpa-standardmethods.org.uk) was adapted to detect viral genome, and a British Standard (BS:EN 14476:2005) was modified to determine virus killing.
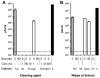
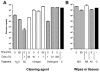
Conclusions/significance: Active ingredients in a number of the cleaning agents, wipes, and tissues tested were able to rapidly render influenza virus nonviable, as determined by plaque assay. Commercially available wipes with a claimed antiviral or antibacterial effect killed or reduced virus infectivity, while nonmicrobiocidal wipes and those containing only low concentrations (<5%) of surfactants showed lower anti-influenza activity. Importantly, however, our findings indicate that it is possible to use common, low-technology agents such as 1% bleach, 10% malt vinegar, or 0.01% washing-up liquid to rapidly and completely inactivate influenza virus. Thus, in the context of the ongoing pandemic, and especially in low-resource settings, the public does not need to source specialized cleaning products, but can rapidly disinfect potentially contaminated surfaces with agents readily available in most homes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- BSEN14476:2005 Chemical disinfectants and antiseptics - virucidal quantitative suspension test for chemical disinfectants and antiseptics used in human medicine - test method and requirements (phase 2, step 1)
-
- FAO. Avian Influenza factsheet. Disinfection. 2007. In: Division APaH, ed.
-
- Abe M, Kaneko K, Ueda A, Otsuka H, Shiosaki K, et al. Effects of several virucidal agents on inactivation of influenza, Newcastle disease, and avian infectious bronchitis viruses in the allantoic fluid of chicken eggs. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2007;60:342–346. - PubMed
-
- De Benedictis P, Beato MS, Capua I. Inactivation of avian influenza viruses by chemical agents and physical conditions: a review. Zoonoses Public Health. 2007;54:51–68. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Collecting, preserving and shipping specimens for the diagnosis of avian influenza A (H5N1) virus infection. 2006. Guide to field operations. Annex 7. Disinfection.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

