Vertebrate Lrig3-ErbB interactions occur in vitro but are unlikely to play a role in Lrig3-dependent inner ear morphogenesis
- PMID: 20126551
- PMCID: PMC2813878
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008981
Vertebrate Lrig3-ErbB interactions occur in vitro but are unlikely to play a role in Lrig3-dependent inner ear morphogenesis
Abstract
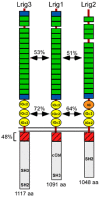
Background: The Lrig genes encode a family of transmembrane proteins that have been implicated in tumorigenesis, psoriasis, neural crest development, and complex tissue morphogenesis. Whether these diverse phenotypes reflect a single underlying cellular mechanism is not known. However, Lrig proteins contain evolutionarily conserved ectodomains harboring both leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin domains, suggesting an ability to bind to common partners. Previous studies revealed that Lrig1 binds to and inhibits members of the ErbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases by inducing receptor internalization and degradation. In addition, other receptor tyrosine kinase binding partners have been identified for both Lrig1 and Lrig3, leaving open the question of whether defective ErbB signaling is responsible for the observed mouse phenotypes.
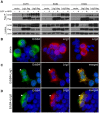
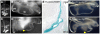
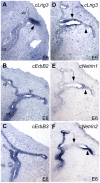
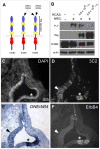
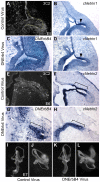
Methodology/principal findings: Here, we report that Lrig3, like Lrig1, is able to interact with ErbB receptors in vitro. We examined the in vivo significance of these interactions in the inner ear, where Lrig3 controls semicircular canal formation by determining the timing and extent of Netrin1 expression in the otic vesicle epithelium. We find that ErbB2 and ErbB3 are present in the early otic epithelium, and that Lrig3 acts cell-autonomously here, as would be predicted if Lrig3 regulates ErbB2/B3 activity. However, inhibition of ErbB activation in the chick otic vesicle has no detectable effect on Netrin gene expression or canal morphogenesis.
Conclusions/significance: Our results suggest that although both Lrig1 and Lrig3 can interact with ErbB receptors in vitro, modulation of Neuregulin signaling is unlikely to contribute to Lrig3-dependent processes of inner ear morphogenesis. These results highlight the similar binding properties of Lrig1 and Lrig3 and underscore the need to determine how these two family members bind to and regulate different receptors to affect diverse aspects of cell behavior in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Ghiglione C, Amundadottir L, Andresdottir M, Bilder D, Diamonti JA, et al. Mechanism of inhibition of the Drosophila and mammalian EGF receptors by the transmembrane protein Kekkon 1. Development. 2003;130:4483–4493. - PubMed
-
- Ghiglione C, Carraway KL, 3rd, Amundadottir LT, Boswell RE, Perrimon N, et al. The transmembrane molecule kekkon 1 acts in a feedback loop to negatively regulate the activity of the Drosophila EGF receptor during oogenesis. Cell. 1999;96:847–856. - PubMed
-
- Goldoni S, Iozzo RA, Kay P, Campbell S, McQuillan A, et al. A soluble ectodomain of LRIG1 inhibits cancer cell growth by attenuating basal and ligand-dependent EGFR activity. Oncogene. 2007;26:368–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

