Comparative study of convolution, superposition, and fast superposition algorithms in conventional radiotherapy, three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy, and intensity modulated radiotherapy techniques for various sites, done on CMS XIO planning system
- PMID: 20126561
- PMCID: PMC2804143
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-6203.48716
Comparative study of convolution, superposition, and fast superposition algorithms in conventional radiotherapy, three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy, and intensity modulated radiotherapy techniques for various sites, done on CMS XIO planning system
Abstract
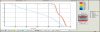
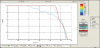
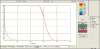
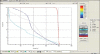
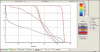
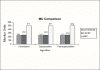
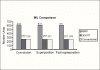
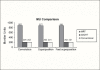
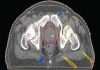
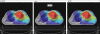
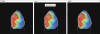
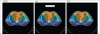
The aim of this study is to compare the dosimetry results that are obtained by using Convolution, Superposition and Fast Superposition algorithms in Conventional Radiotherapy, Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy (3D-CRT), and Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT) for different sites, and to study the suitability of algorithms with respect to site and technique. For each of the Conventional, 3D-CRT, and IMRT techniques, four different sites, namely, Lung, Esophagus, Prostate, and Hypopharynx were analyzed. Treatment plans were created using 6MV Photon beam quality using the CMS XiO (Computerized Medical System, St.Louis, MO) treatment planning system. The maximum percentage of variation recorded between algorithms was 3.7% in case of Ca.Lung, for the IMRT Technique. Statistical analysis was performed by comparing the mean relative difference, Conformity Index, and Homogeneity Index for target structures. The fast superposition algorithm showed excellent results for lung and esophagus cases for all techniques. For the prostate, the superposition algorithm showed better results in all techniques. In the conventional case of the hypopharynx, the convolution algorithm was good. In case of Ca. Lung, Ca Prostate, Ca Esophagus, and Ca Hypopharynx, OARs got more doses with the superposition algorithm; this progressively decreased for fast superposition and convolution algorithms, respectively. According to this study the dosimetric results using different algorithms led to significant variation and therefore care had to be taken while evaluating treatment plans. The choice of a dose calculation algorithm may in certain cases even influence clinical results.
Keywords: Algorithm; conformity index; homogenity index; treatment planning system.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures








Similar articles
-
SU-E-T-601: Dosimetric Evaluation of the Parameter Variation with Varying Calculation Grid Size in the IMRT Cases.Med Phys. 2012 Jun;39(6Part19):3844. doi: 10.1118/1.4735690. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 28517093
-
On the use of a convolution-superposition algorithm for plan checking in lung stereotactic body radiation therapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016 Sep 8;17(5):99-110. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i5.6186. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 27685114 Free PMC article.
-
Performance Evaluation of Algorithms in Lung IMRT: A comparison of Monte Carlo, Pencil Beam, Superposition, Fast Superposition and Convolution Algorithms.J Biomed Phys Eng. 2016 Sep 1;6(3):127-138. eCollection 2016 Sep. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2016. PMID: 27853720 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric Comparison of Different Dose Calculation Algorithms in Postmastectomy Breast Cancer Patients Using Conformal Planning Techniques.J Med Phys. 2023 Apr-Jun;48(2):136-145. doi: 10.4103/jmp.jmp_28_23. Epub 2023 Jun 29. J Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 37576097 Free PMC article.
-
[Dosimetric comparison of different techniques for external beam accelerated partial breast irradiation].Magy Onkol. 2016 Nov 29;60(4):305-311. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Magy Onkol. 2016. PMID: 27898749 Review. Hungarian.
Cited by
-
Dosimetric Evaluation of Different Algorithms on Heterogeneous Slab Phantom Using CMS XiO and MONACO Treatment Planning System for 4MV, 6MV and 15MV Beam Energy: An Institutional Study.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Dec 1;25(12):4381-4389. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.12.4381. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 39733431 Free PMC article.
-
Commissioning and initial acceptance tests for a commercial convolution dose calculation algorithm for radiotherapy treatment planning in comparison with Monte Carlo simulation and measurement.J Med Phys. 2012 Jul;37(3):145-50. doi: 10.4103/0971-6203.99237. J Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22973081 Free PMC article.
-
EGSnrc application for IMRT planning.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020 Mar-Apr;25(2):217-226. doi: 10.1016/j.rpor.2020.01.004. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020. PMID: 32194347 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Inhomogeneity Correction Performed by Radiotherapy Treatment Planning System.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022 Dec 1;23(12):4155-4162. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.12.4155. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022. PMID: 36579997 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric comparison of different inhomogeneity correction algorithms for external photon beam dose calculations.J Med Phys. 2013 Apr;38(2):74-81. doi: 10.4103/0971-6203.111310. J Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23776310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garcia-Vicente F, Minambres A, Jerez I, Modocell I, Perez L, Torres JJ. Experimental validation tests of Fast Fourier Transform convolution and multigrid superposition algorithm for dose calculation in low density media. Radiother Oncol. 2003;67:239–49. - PubMed
-
- Vanderstraeten B, Reynaert N, Paelinck L, Madani I, De Wagter C, De Gersem W, et al. Accuracy of patient dose calculation for lung IMRT: A comparison of Monte Carlo, convolution/superposition, and pencil beam computations. Med Phys. 2006;33:3149. - PubMed
-
- Animesh Advantages of multiple algorithms support in treatment planning system for external beam dose calculations. J Cancer Res Ther. 2005;1:12–20. - PubMed
-
- De Neve W, Wu Y, Ezzell G. “Practical IMRT Planning”. In: Bortfeld T, Schmidt-Ullrich R, De Nere W, Wazer DE, editors. Image-guided IMRT. Berlin: Springer; 2006. pp. 49–54.
-
- Mackie TR, Scrimger JW, Battista JJ. A convolution method of calculating dose for 15 MV x-rays. Med Phys. 1985;12:188–96. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
